What is Aluminum? Aluminum is one type of metal element. Its element symbol is Al, with an atomic number of 13 and a relative atomic mass of 26.98154. it is solid at room temperature and has a silvery white luster. Aluminum ranks third in the earth’s crust, second only to oxygen and silicon, with a content of 8.3%. It is the most abundant metal element in the earth’s crust. Among metal varieties, it is the second largest type of metal after steel.
Advantages of Aluminum
Aluminum and its alloys have many advantages, such as lightweight, corrosion resistance, good machinability and more. Below are some of their obvious advantages:
Lightweight and strong
The density of steel is about 7.9, while the density of aluminum is about 2.7. The weight of aluminum is only one-third of that of steel at the same volume; on the other hand, the strength of aluminum is about 70% of that of general structural steel. Therefore, aluminum is a material with higher strength per unit weight.
Good corrosion resistance
Aluminum can naturally form a dense layer of aluminum oxide in the air, which is like a protective film. It is difficult for corrosion to develop deeper than this protective film, which gives aluminum good corrosion resistance. In a humid or corrosive environment, aluminum products can maintain stability and durability for a long time.
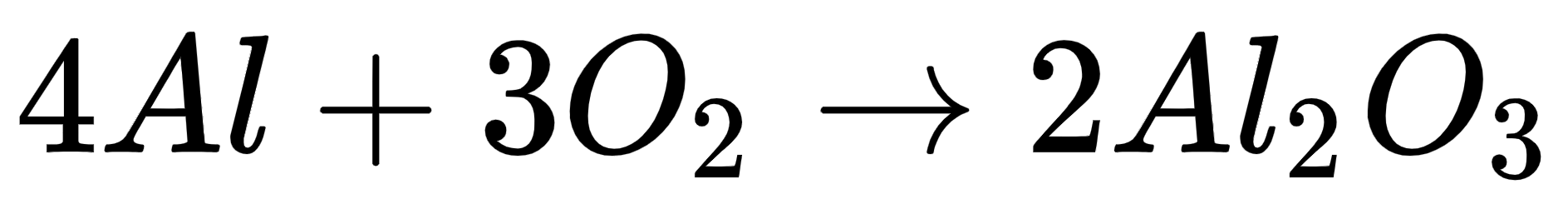
Good electrical conductivity
The conductivity of aluminum is only worse than that of silver, copper and gold. Although its conductivity is only 2/3 of copper, its density is only 1/3. To transport the same amount of electricity, the quality of aluminum wire is only 46%of copper wire. The oxide film on the aluminum surface is corrosion-resistant and has a certain degree of insulation.
Good Thermal conductivity
Aluminum is a lightweight thermally conductive metal material with a thermal conductivity of approximately 237 W/(m·K), which is only slightly worse than silver and copper.
Strength at low temperatures
Aluminum and its alloys are the best low-temperature materials. Steel and nickel alloys have obvious low-temperature brittleness, which means although their strength properties increase with decreasing temperature, their plasticity and toughness decrease. However, aluminum and its alloys are very different. They do not have any low-temperature brittleness. All their mechanical properties increase significantly with decreasing temperature.
| Alloy | condition | Temp. ℃ | Tensile StrengthN/mm2 | Yield Strength N/mm2 |
| 5050 | O | -200 | 255 | 70 |
| -80 | 150 | 60 | ||
| -30 | 145 | 55 | ||
| 25 | 145 | 55 | ||
| 150 | 145 | 55 | ||
| 5454 | O | -200 | 370 | 130 |
| -80 | 255 | 115 | ||
| -30 | 250 | 115 | ||
| 25 | 250 | 115 | ||
| 150 | 250 | 115 | ||
| 6101 | O | -200 | 296 | 287 |
| -80 | 248 | 207 | ||
| -30 | 234 | 200 | ||
| 25 | 221 | 193 | ||
| 150 | 193 | 172 |
Good machinability
Aluminum has good ductility, which is second only to gold and silver. It can be made into aluminum foil thinner than 0.01 mm at a temperature of 100℃ to 150℃.
Aluminum alloy has good machinability and is easy to process into various shapes and structures. It can be formed by various processing techniques such as extrusion, casting, forging, etc. This allows aluminum alloys to have great flexibility in the field of design and manufacturing and can meet the needs of different products. In addition, aluminum alloy can also be assembled through welding and connection to achieve more complex structures.
Easy to recycle
The melting point of aluminum is 660℃, which makes it much easier to recycle. Data shows that the recycling rate of aluminum cans is as high as 68%, while plastics are only about 3%. The energy consumption of aluminum recycling is also much lower. The energy consumption of producing recycled aluminum is only about 5% of that of original aluminum.
Applications of Aluminum
In the past fifty years, aluminum has become one of the most widely used metals in the world. In the construction industry, aluminum is widely used due to its stability in the air and its excellent appearance after anodizing. Aluminum alloy materials are also widely used in aviation and defense military industries. In power transmission, aluminum cables reinforced with high-strength steel wires are often used. In some places, aluminum cables are used instead because copper cables are often stolen due to their high prices. Container transportation, daily necessities, household appliances, mechanical equipment, etc. all require a large amount of aluminum.






