Press fit tolerance, also known as interference fit tolerance, refers to the allowable range of sizes for mating components in which one part (usually a shaft) is slightly larger than the hole it pairing, resulting in a tight, frictional connection. This article will discuss some basics of press fit tolerance including what is fit, fit tolerance and press fit tolerance.
What are Fits?
Fits are the relationships between the tolerance zone of pairing holes and shafts at the same basic size. Or we can say that fits are the clearance between the hole and shaft pairing. The clearance can be both positive and negative. The size of the clearance determines whether the two paired parts can move or rotate independently of each other or, are temporarily or permanently connected.
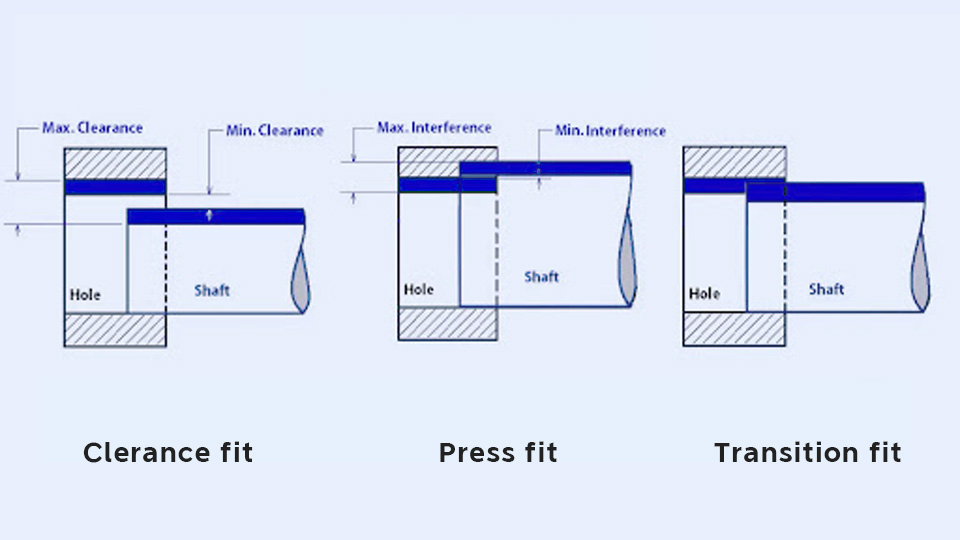
There are three types of fits: clearance fit, transition fit, and press fit(interference fit).
Clearance fit: The tolerance zone of the hole is above that of the shaft, in other words, the hole is larger than the shaft.
Press fit: The tolerance zone of the hole is below that of the shaft, in other words, the shaft is larger than the hole.
Transition fit: The tolerance zones of the hole and shaft overlap. Any pair of holes and shafts may achieve a clearance or a press fit.
What is Fit Tolerance?
Fit tolerance is the degree of clearance or interference between the shaft and hole. It determines how tightly or loosely these parts join together. For clearance fit, the fit tolerance is the difference between the maximum clearance and the minimum clearance; for interference fit, the fit tolerance is the difference between the minimum interference and the maximum interference; for transition fit, the fit tolerance is the difference between the maximum clearance and the maximum interference.
Hole-basis System
The hole-basis system is a system that pairs the tolerance zone of a hole with a fixed basic deviation and the tolerance zone of a shaft with a different basic deviation. The hole in the basic hole system is called a reference hole, and its basic deviation code is “H”. The H7p6 mentioned below is the basic hole system used.
Shaft-basis Syetem
The shaft-basis system is a system that pairs the tolerance zone of a shaft with a fixed basic deviation with that of a hole with a different basic deviation. The shaft in the basic shaft system is called the datum shaft, and its basic deviation code is “h”.
What is Press Fit Tolerance?
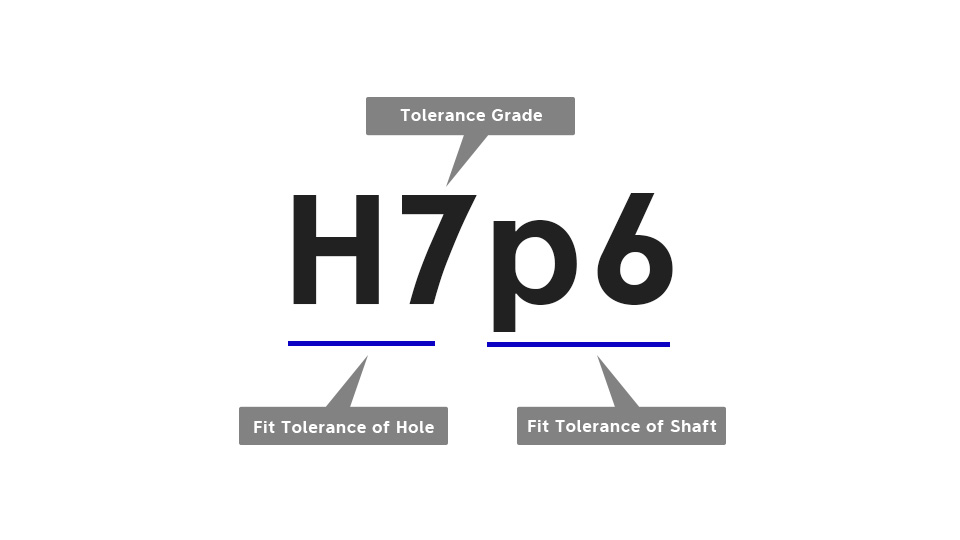
From the above paragraph, we know that the fit tolerance is up to the tolerance zone of the shaft and the hole, so it is easy to learn that the symbol of the fit tolerance includes the description of the tolerance zone of the shaft and the hole. Taking H7p6 as an example, H7 describes the tolerance zone of the hole, and p6 is the tolerance zone of the shaft. The letters and numbers represent the tolerance range and tolerance level.
Tolerance levels define the tolerance range of different part sizes. According to the CNS standard, it includes 20 levels, IT01, IT0, IT1…IT17, and IT18, among which IT01 represents the smallest tolerance range. Parts processed according to tolerance level IT01 are the most precise, while IT18 is the opposite.
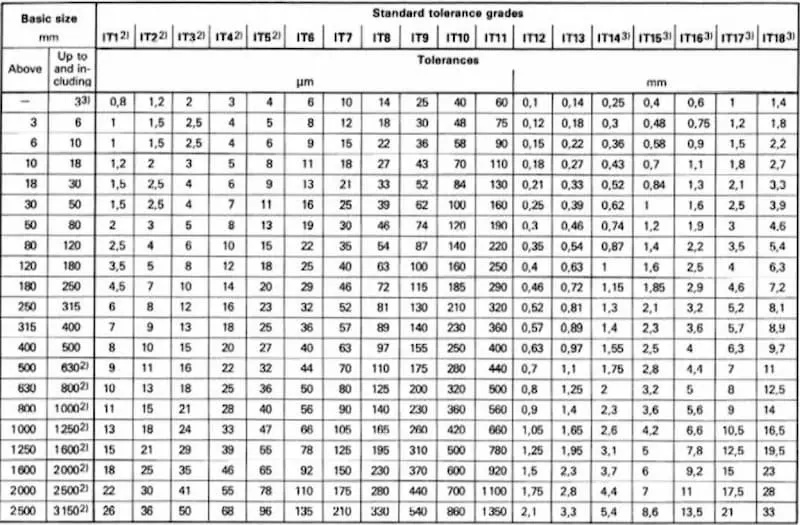
You may think that the tolerance class table determines the size of the tolerance range, so why do we need the tolerance range letter? Its purpose is to specify the location of the tolerance zone.
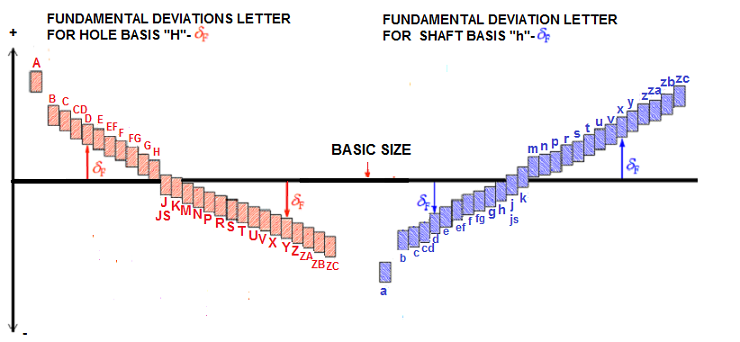
As we can see from above, the uppercase letters represent the fundamental deviation of the hole, and the lowercase letters represent the fundamental deviation of the shaft. There are 28 positions from A to ZC relative to the basic size. The letter indicates their position relative to the basic size, which includes positive or negative deviation.
Looking at the H7p6, we assume that the base size of the shaft and hole is 30mm. The initial letter of H7 is an uppercase letter, which means that this fit tolerance describes the tolerance zone of the hole. H means that the basic size is set as the origin. 7 is the tolerance level. From the CNS tolerance level table, we know that the upper and lower tolerance limits corresponding to the base size of 30mm are within 0.021mm, so the H7 tolerance is 0 ~ + 0.021mm, and the hole size range is 30 mm-30.021 mm.
The letter p6 is lowercase, which means that this fit tolerance describes the tolerance zone of the shaft. p means that the point larger than the basic size + 0.035mm is used as the origin. From the CNS tolerance level table, we know that the tolerance range corresponding to the base size of 30mm is 0.013mm. Therefore, the g6 tolerance is +0.022mm ~ +0.035mm, and the shaft size range is 30.022mm-30.035mm.
Therefore, the fit tolerance of H7p6 is the press fit tolerance.
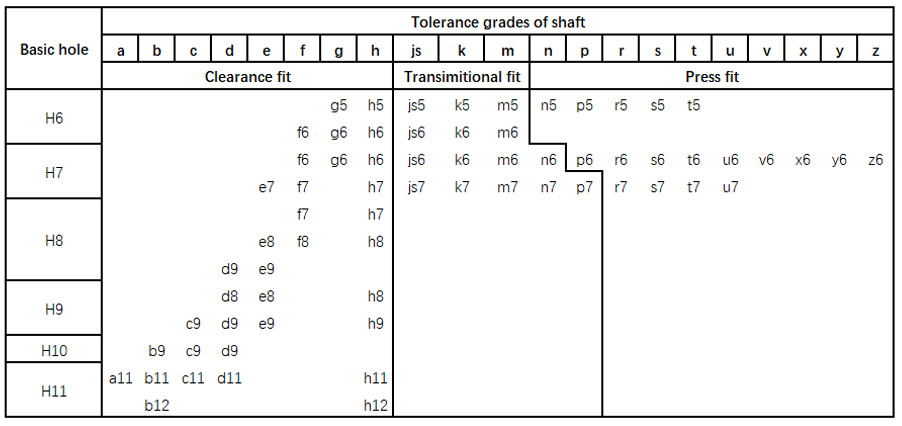
Press Fit Tolerance Chart
The table below shows the common press fit and tolerance grades with the hole basis system.