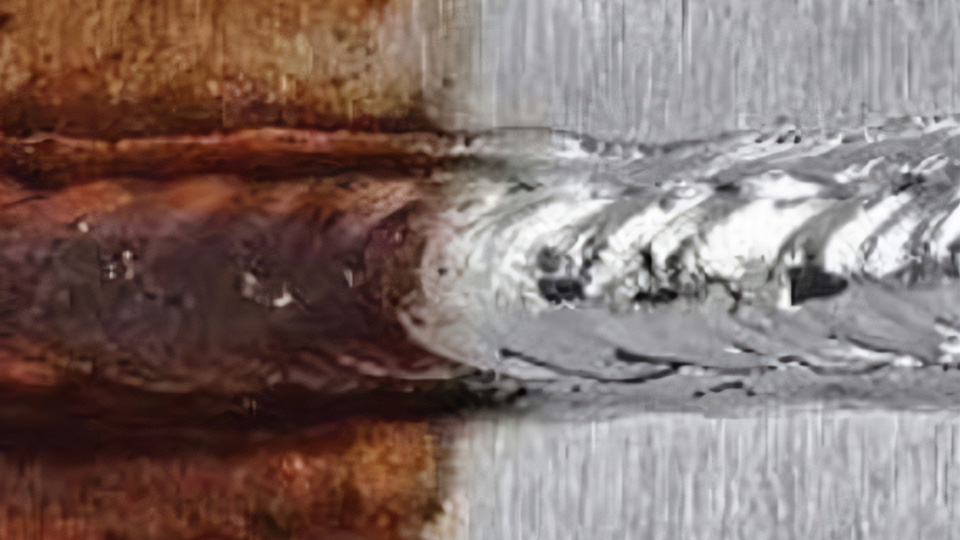
After welding a stainless steel part, engineers typically clean the welded area using various chemical agents, including nitric acid and pickling pastes that contain hydrofluoric acid. This process is known as passivation. This article will discuss what is weld passivation and how it works.
What is Passivation?
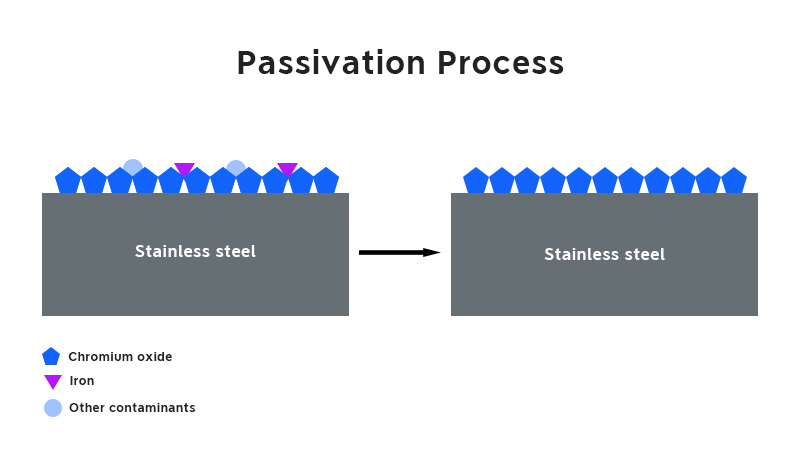
Passivation is a process that uses a strong oxidizing agent to create a dense, protective oxide layer on a metal’s surface. In stainless steel, passivation involves using an acidic solution to remove surface iron and other contaminants. This treatment forms a thicker layer of chromium oxide, which greatly improves the stainless steel’s resistance to corrosion.
History of Passivation
In the 1800s, the chemist Christian Friedrich Schönbein discovered the effects of passivation on metals. He immersed iron in concentrated nitric acid and compared it to iron that had not been treated. The treated iron was virtually chemically unreactive compared to the untreated iron.
As welding and passivation of stainless steel became more popular, the environmental and safety impacts of using nitric acid became more apparent.19 In the early 1900s, a German brewing company found citric acid to be a safer, non-toxic alternative to passivation. In 1990, citric acid had replaced nitric acid in many applications in large quantities. Today, both acids are used in modern passivation processes.
What Does Weld Passivation Do?
Stainless steel is primarily made of iron, chromium, and nickel. Chromium provides its corrosion resistance: when chromium is exposed to oxygen, it forms a thin layer of chromium oxide on the stainless steel’s surface, protecting the iron underneath from rust. During welding, however, localized heating can damage this protective oxide layer, making the weld area more susceptible to contamination. Without passivation, environmental contaminants, like chlorides, can react with exposed iron on the surface and initiate corrosion. Once corrosion begins, it can spread through the weld area and into the entire component.
Passivation helps slow or prevent corrosion in 2 ways. First, It allows iron and iron oxides to dissolve more readily than chromium and its oxides, this process removes the iron-rich layer and increases chromium concentration at the surface. Second, Passivation enhances the oxidation process of chromium to form a thicker inert oxide layer, which protects the underlying metal from environmental contaminants.
After fabrication and welding, passivation is the next critical step for stainless steel parts. Key benefits of weld passivation include:
- Removing contaminants from the weld surface
- Extending the lifespan of both the weld and the entire component
- Forming a protective chemical barrier against rust and corrosion
Weld Passivation Methods
Weld passivation can be divided into several types according to their operations.
Pickling paste
Pickling passivation paste is a viscous liquid (gel), which is mainly made of nitric acid, hydrofluoric acid, corrosion inhibitor, thickener, etc. in a certain proportion. It is applied to the weld seam and washed off after about 30 to 60 minutes.
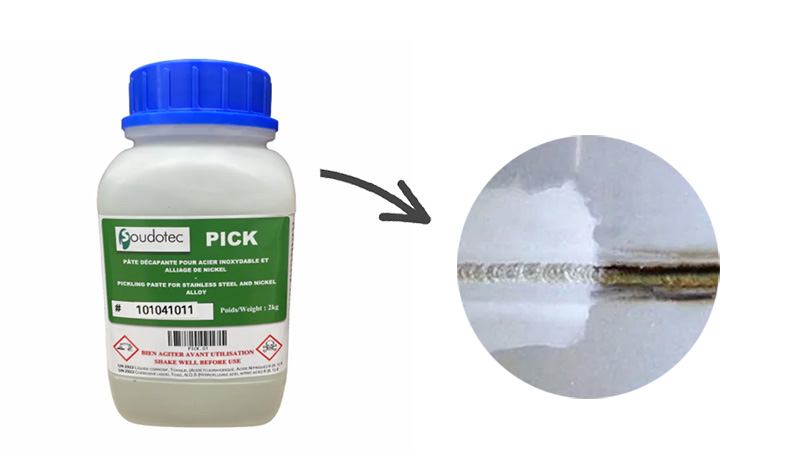

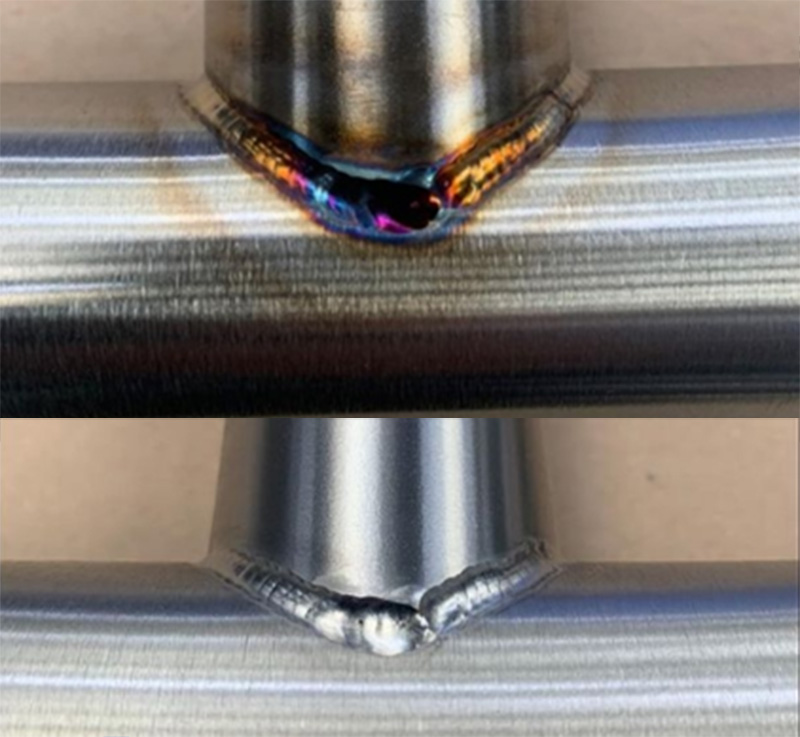
Washing off the paste is particularly challenging, as the resulting wastewater is highly polluting and cannot be directly washed down the drain. Instead, the wastewater must be carefully collected and taken to a disposal facility. Over the years, the harmful effects of pickling paste have drawn increasing attention from workplace safety authorities, leading to stricter regulations around its use. While pickling paste does create a corrosion-resistant weld seam, it leaves a matte appearance on treated areas, often requiring an additional polishing process, which adds time to the process. Although pickling paste is widely used, we anticipate that modern, safer alternatives, such as electrochemical weld cleaning, will become more prominent—a shift that benefits both human health and the environment.
Dip and spray pickling
Dip pickling and passivation involve dipping the whole piece into a bath with pickling fluid. The items will get a nice, evenly pickled surface on both their internal and external surfaces. Since the items are completely immersed, this method is highly effective with tubes and workpieces with narrow areas and corners that are difficult to reach manually.
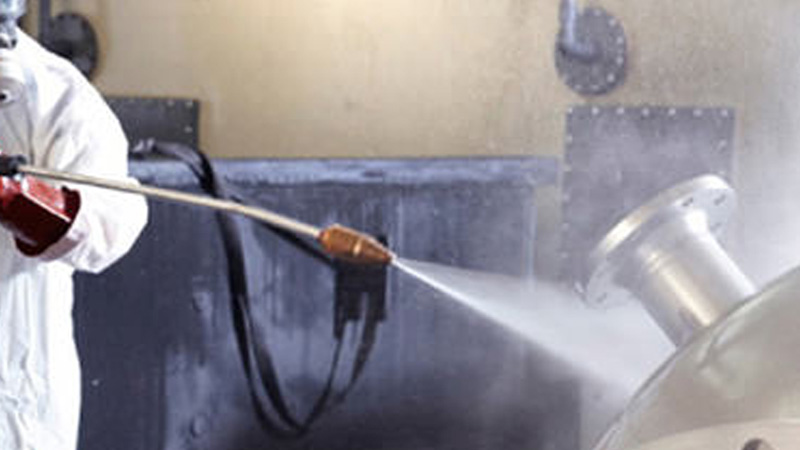

Spray pickling is advantageous for very large items, as the pickling fluid is sprayed onto the surface and rinsed off, usually after 30-60 minutes. Due to the environmental laws and safety requirements, spray pickling is performed by professionals who collect and dispose of the acids and wastewater.
Spray pickling is often used if the item is too big for dip pickling. It can also be performed with a mobile pickling plant, where a professional will spray pickle the item on-site if it is too complicated to move.
Electrochemical weld passivation
Electrochemical weld cleaning and passivation is a highly effective way of removing oxides from stainless steel welds. The method combines phosphorus-based acids and electricity in a process that results in instantaneous cleaning and passivation.

Phosphoric acids are non-toxic and can be found in fizzy drinks and common household cleaning items – and are not even remotely as harmful as the pickling paste. There is no need to clean the surface with water which makes your process much simpler – you will avoid all the hassle with wastewater disposal.
Process of Weld Passivation
Taking the weld passivation of stainless steel 304 as an example, the main operation steps are:
1. Pretreatment
Before pickling and passivation treatment, the surface of 304 stainless steel needs to be pretreated. The pretreatment methods include degreasing and cleaning, etc., and the purpose is to remove the residual grease and contaminants on the surface.
2. Passivation
Put the 304 stainless steel in the pickling agent and soak it. The pickling agent will dissolve the surface oxide scale and weld spot. The pickling time needs to be determined according to the actual situation, generally controlled between 5-30 minutes.
Or, apply passivation paste to the weld and let it stand for 15 minutes to 60 minutes;
3. Neutralization
Use an alkali solution to neutralize the acidic passivation liquid remaining on the surface to avoid corrosion caused by acid residues and damage to the passivation film. For parts with complex structures such as fine seams, 5% sodium hydroxide can be used for neutralization.
4. Drying
According to the conditions, use methods like wiping or blowing to make the parts dry.
When to Consider Weld Passivation
After welding, cutting, and any other CNC machining operations are done, the passivation process can begin. Stainless steel is inherently corrosion and rust-resistant, but several different processes can introduce potential contaminants that will inhibit the formation of the protective oxide layer during the manufacturing process. This is the time to introduce passivation to improve the corrosion resistance of the weld area.
Put Your Custom Parts into Production Today!
Some of the factors that may inhibit oxide film formation and reduce the corrosion resistance of stainless steel parts include:
- Foreign matter such as dirt, dust, oil, swarf, and coating materials.
- Different sulfides are added to stainless steel to make it more machine-friendly.
- Iron chips can be embedded in stainless steel from blades, discs, and other cutting tools during the cutting process.
If stainless steel parts are painted or powder coated, passivation is not necessary.
Quality Testing of Weld Passivation
There are several methods for testing the effectiveness of passivation, but it’s important to note that not all methods are suitable for every stainless steel grade. Various testing methods are outlined in ASTM International standards, including:
- ASTM A380: This standard describes best practices for cleaning, descaling, and passivating stainless steel parts, equipment, and systems.
- ASTM A967: This standard details passivation test methods and acceptance criteria, as well as procedures to ensure effective passivation.
- Water immersion test: In this test, the passivated component is submerged in distilled water to detect impurities, such as free iron, on the anode surface.
- Salt spray test: This test evaluates the corrosion resistance of stainless steel by placing the specimen in a salt spray chamber filled with 5% sodium chloride (NaCl) solution at a temperature of 95°F.
- High humidity test: This test requires specialized laboratory equipment, including a humidity chamber maintained at 97% (±3%) humidity and a temperature of 100°F (±5°F) for a minimum of 24 hours. The test piece must be immersed in acetone or methanol and then dried in an inert atmosphere or dehydrating container.
- Blue point test: Prepare a solution by mixing 1 gram of potassium ferrocyanide (K₃Fe(CN)₆) with 3 ml of nitric acid (65%–85%) and 100 ml of water (preferably prepared on-site). Soak filter paper in this solution and apply it to the surface to be tested, or drop the solution directly onto the surface. Observe the surface condition within 30 seconds; if no blue precipitate appears, the treatment is deemed successful. Rinse the test solution off after the assessment.
Conclusion
Weld passivation is an essential process that is used to enhance the corrosion resistance of stainless steel after welding, and this process ensures their longevity and reliability in various applications. As industry standards evolve, safer alternatives like electrochemical cleaning are becoming increasingly popular, providing environmentally friendly options compared to traditional pickling methods.






