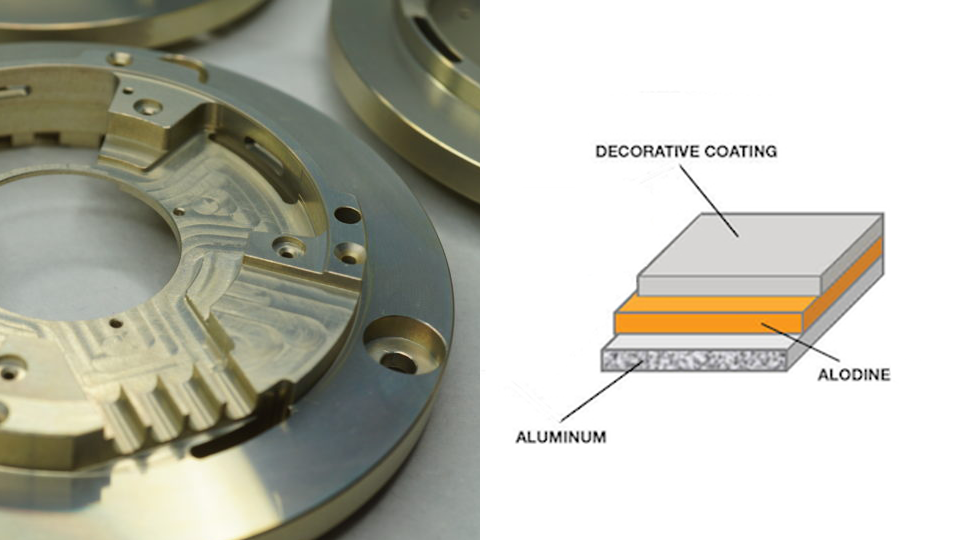
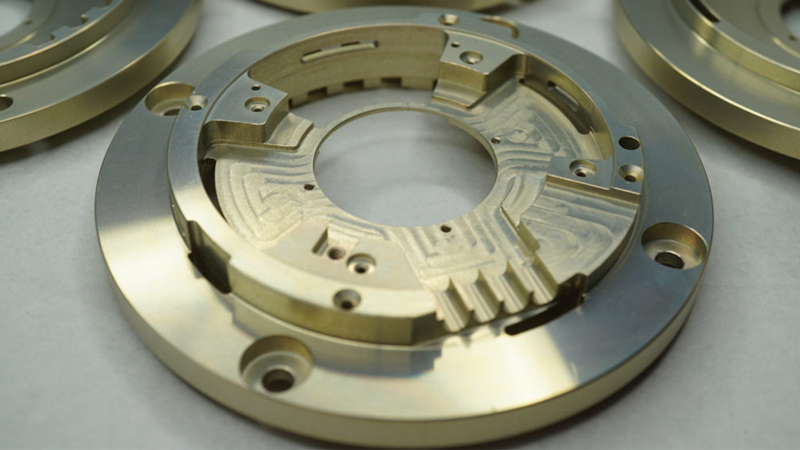
Alodine coating, also known as chromate conversion coating, is a widely used method for enhancing the surface properties of aluminum alloys. This treatment forms a protective layer on the metal surface to improve corrosion resistance, better paint adhesion, and other significant functional benefits. It is a critical process of mechanical parts used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics where the durability and performance of metal components are critical factors.
What is Alodine Coating?
Alodine coating involves applying a chemical solution containing chromates on the surface of aluminum alloys. This surface finishing process forms a thin, protective conversion coating that adheres to the surface of the metal part to improve its corrosion resistance and prepare it for further finishing such as painting or anodizing. Compared to anodizing, Alodine coating is faster and does not require electrical current, which makes it a more affordable and efficient choice for many price-sensitive clients.
Solutions for Alodine Coating
The type of Alodine solution used depends on the material type, primer, and specific color requirements. Common solutions include:
- Alodine 600: Produces a yellow coating on aluminum surfaces.
- Alodine 1200, 1200S and 1201: Produces a light gold to brownish-yellow finish.
- Alodine 1000 and 1500: Keeps the aluminum surface in its natural metallic color.

The typical formulations for these solutions are detailed in the table below:
| Solution Type | Powder Content (oz) | Distilled Water (gal) | Notes |
| Alodine 600 | 3 | 1 | Add 2% Alodine Toner 22 to adjust pH to 1.5–2.0 |
| Alodine 1000 | 0.35–0.44 | 1 | |
| Alodine 1200 | 3 | 1 | Add nitric acid to adjust pH to 1.5–1.9 |
| Alodine 1200S | 1.9–2.1 | 1 |
Types of Alodine Coating
Different types of Alodine coatings are available, each tailored to specific requirements. The most common classifications are based on the MIL-DTL-5541 standard, which specifies two primary types:
Type 1 (Hexavalent Chromium Coatings): These coatings contain hexavalent chromium and are highly effective in providing corrosion resistance. However, due to environmental and health concerns, their use has been increasingly regulated.
Type 2 (Trivalent Chromium Coatings): As an alternative to Type 1, Type 2 coatings use trivalent chromium, which offers similar performance with reduced environmental impact. These coatings are often transparent and have become the preferred choice in many industries.
Alodine Processes
The implementation of Alodine coating can be carried out through three primary methods: immersion, spraying, and brushing. Brushing is the most commonly used approach in aircraft structure repairs. The specific steps for the Alodine process are as follows:
1. Surface Cleaning
Before applying the solution, the aluminum surface must be thoroughly cleaned to ensure optimal coating adhesion.
For areas with oil residues (such as aviation hydraulic oils), use a clean cloth or sponge soaked in solvents like MEK, acetone, or MIBK to wipe the surface clean. If no oils are present, deionized water can be used to remove impurities. For specific applications like shot-peened surfaces, use a Scotch-Brite pad soaked in deionized water to clean the surface as per BAC 5748 standards. This involves multiple cleaning passes, each using a new pad, followed by rinsing with deionized water and drying with a clean cloth.
After cleaning, the surface should be bright and free of contaminants. Allow at least 15 minutes for the surface to dry completely before proceeding.
2. Applying Solution
In cases where the work area is near sensitive components like composite honeycomb cores, wires, or gaps, ensure proper masking to prevent accidental exposure to the Alodine solution.
Alodine 600/1200 Series: Use pneumatic spray guns or nylon brushes to coat the work area with the Alodine solution evenly. Keep the surface wet for 2–3 minutes. A golden or yellow-brown color will appear, indicating the formation of the protective layer. Wipe away excess solution with a clean cloth or sponge. If uneven coloration or residue is observed, lightly sand the area with 600-grit sandpaper, rinse with deionized water, and reapply the solution.
Alodine 1000 Series: Similar to the 600/1200 series, apply the solution uniformly and keep the surface wet for 3–5 minutes. Avoid direct sunlight during application. Any issues such as solution pooling or powdery residue require the same remediation steps: light sanding, rinsing, and reapplication.

3. Cleaning and Drying
Clean the treated surface with a water-soaked cloth or sponge to remove excess chemicals. Handle the soft and easily damaged coating with care. Use a clean, dry cloth to wipe the surface and allow it to dry at temperatures up to 54°C (130°F). Alternatively, dry the surface at 44–54°C (110–130°F) for 20–35 minutes to enhance corrosion resistance. Once dried, apply the primer paint promptly, ideally within 16 hours, to maximize coating protection.
Benefits of Alodine Coating
Alodine coating offers several advantages, making it a popular choice for aluminum surface finishing:
Thin and porous oxide layer: The Alodine conversion coating is typically thin, measuring around 0.5–4 µm. Its soft and porous nature provides excellent paint and coating adhesion without altering the mechanical properties or dimensions of the workpiece. This makes it an ideal primer layer for further surface treatments.
Cost-effectiveness process: The Alodine process is quick, does not require electrical power, and involves simple equipment. These factors contribute to its low production costs, while still delivering a strong, corrosion-resistant finish.
Conductive coating: Unlike some other surface treatments, Alodine produces a conductive coating. This property helps stabilize contact resistance and ensures effective electrical conductivity, crucial for applications in the electronics and aerospace industries.
Make Your Idea Take Shape!
Low-temperature requirement: Most Alodine treatment steps are conducted at room temperature, except for the alkaline cleaning stage, which typically operates at around 60°C. This reduces energy consumption and minimizes environmental pollution in the production environment.
Durable solution: Alodine solutions are stable, have a long usage life, and are easy to maintain. These features make them suitable for large-scale, continuous production with minimal disruptions.
Improved corrosion resistance: The Alodine coating provides exceptional protection against corrosion, significantly extending the lifespan of aluminum components even in harsh environments.
Enhanced fatigue performance: Research indicates that Alodine can help predict and improve the fatigue life of aluminum alloys under varying stress conditions. By quantifying corrosion pits as equivalent elliptical surface cracks, the treatment aids in a more accurate reflection of the material’s real-world performance.
Applications of Alodine Coating
Alodine coating is widely used across various industries, including:
- Aerospace: Protecting aluminum airframe components from corrosion.
- Automotive: Enhancing the durability of aluminum parts exposed to harsh environments.
- Electronics: Improving the performance and longevity of enclosures and heat sinks.
- Marine: Providing corrosion resistance for aluminum parts used in coastal or underwater settings.

Alodine vs Anodize
Alodine provides corrosion resistance and enhances the adhesion of the coating. It creates a thin, soft layer that typically ranges from 0.5 to 4 μm in thickness. This process is energy-efficient, requiring less power to complete, and it operates at room temperature. However, Alodine offers limited color options, typically in yellow, brown-yellow, or natural tones, which can restrict its aesthetic appeal.
On the other hand, anodizing is a more complex electrochemical process that produces a thicker, harder coating, typically between 5 and 25 μm, the thickness depends on which type of anodizing is applied. This coating is more durable than alodine, which offers higher surface hardness and better resistance to wear and scratching. Anodizing is a non-conductive process, which can be advantageous in parts that require electrical insulation. However, it needs more energy due to the electrochemical process and operates at high temperatures. One of anodizing’s greatest strengths is its wide color selection, ranging from clear to a variety of vibrant shades, which provides more versatility in aesthetics.
| Factors | Alodine | Anodize |
| Color options | Limited. Yellow, brown-yellow or natural color | Wide color selection |
| Thickness | 0.5-4μm | 5-25μm |
| Surface hardness | Soft | Hard |
| Electrical conductivity | Conductive | Non-conductive |
| Temperature | Room temp. | Higher temp. |
| Energy consumption | Low | High |
Conclusion
Alodine surface finishing is a versatile and effective method for enhancing the properties of aluminum and its alloys. By providing superior corrosion resistance, improved paint adhesion, and compliance with industry standards, it plays a vital role in the manufacturing of durable and high-performance components. Understanding the types, benefits, and applications of Alodine coating can help manufacturers make informed decisions about their surface finishing needs.