5052 and 6061 aluminum are two commonly used aluminum alloys with unique strengths. 5052 is known for its high corrosion resistance, making it ideal for marine applications. 6061 aluminum offers greater strength, especially when heat-treated, and is used in structural and precision applications like aerospace. This article will examine the key differences in properties, cost, and applications between 5052 and 6061, offering insights into selecting the right alloy based on specific project requirements.
What is Aluminum 5052?
Aluminum 5052 is a typical grade of the 5000 series, composed of 2.2%-2.8% magnesium, despite magnesium, it has small amounts of Mn, Cr, and Ti. It is an aluminum-based alloy that can not get upgraded mechanical properties through heat treatments. The alloy has moderate strength, good corrosion resistance, and good weldability and machinability. The common tempers for 5052 aluminum alloy include annealed(O temper), H32, H34, H36, and H38.
Table 1. Composition specification of Aluminum 5052(%)
| Alloy | Al | Mg | Fe | Si | Cu | Mn | Cr | Zn | |
| 5052 | Remainder | 2.2-2.8 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.10 | |
Table 2. Properties of aluminum 5052 in different tempers
| Properties/Alloys | Tensile strength, MPa | Yield strength, MPa | Elongation, % |
| 5052-O | 170 – 215 | 65 | 13-18 |
| 5052-H32 | 215 – 265 | 160 | 4-11 |
| 5052-H34 | 235 – 285 | 180 | 3-10 |
| 5052-H36 | 255 – 305 | 200 | 2-4 |
| 5052-H38 | ≥ 270 | 220 | 2-4 |
What is Aluminum 6061?
Aluminum 6061 is a typical heat-treatable aluminum-based alloy, it is part of the 6000 series and primarily composed of 0.8%-1.2% magnesium and 0.4%-0.8% silicon. It has good formability, weldability, machinability, resistance and moderate strength. The common tempers for 5052 aluminum include temper O, T4, T5/651.
Table 3. Composition specification of Aluminum 6061(%)
| Alloy | Al | Mg | Fe | Si | Cu | Mn | Cr | Zn | Ti | |
| 6061 | Remainder | 0.8-1.2 | 0.70 | 0.4-0.8 | 0.15-0.4 | ≤0.15 | 0.04-0.35 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.15 | |
Table 4. Properties of aluminum 6061 in different tempers
| Properties/Alloys | Tensile strength, MPa | Yield strength, MPa | Elongation, % |
| 6061-O | 125 | 55 | 25-30 |
| 5052-T4 | 207 | 110 | 16 |
| 5052-T6/T651 | 310 | 276 | 12 |
Aluminum 5052 vs 6061: An Ultimate Comparison
Choosing between 5052 and 6061 for CNC machining is an essential step for high-quality aluminum prototypes. You should carefully understand the critical differences between these two grades and then make a decision based on your application requirements. For example, when your aluminum parts are set as fuel tanks, the grade that is better at corrosion resistance may be your ideal choice.
Elemental composition
Aluminum 5052 and 6061 have key compositional differences impacting their properties and applications. With higher magnesium (2.2-2.8%) and chromium (0.15-0.35%) content, 5052 is better in corrosion resistance and this property makes it more suitable for moisture and chemical environments such as marine. On the other hand, 6061 contains a higher content of silicon (0.4-0.8%), which enables it to be heat treated to get upgradable mechanical properties.
Table 5. Composition comparison of Aluminum 5052 and 6061(%)
| Property/Grades | 5052 | 6061 |
| Yield Strength, MPa | 228 | 310 |
| Yield Strength, MPa | 193 | 276 |
| Elastic Modulus, GPa | 70.3 | 68.9 |
| Fatigue Strength, MPa | 117 | 62 |
Mechanical properties: strength and more
The mechanical properties of aluminum alloys are essential in determining their suitability for different applications. Let’s compare the key mechanical properties of aluminum 5052 and 6061.
Table 6. Properties of aluminum 5052 and 6061
| Property | 5052 | 6061 |
| Composition | Aluminum-Magnesium | Aluminum-Silicon-Magnesium |
| Chloride resistance | Good | Moderate |
| Acid resistance | Good | Poor |
| Salt spray test | Slight pitting | Significant pitting |
Aluminum 5052 and 6061 alloys have distinct mechanical properties suited for different applications. Tensile strength is the maximum stress an alloy can handle before breaking, with 6061 outperforming 5052 at 310 MPa, making it ideal for structural applications. Yield strength, the point where permanent deformation begins, is also higher in 6061 (276 MPa) than in 5052 (193 MPa), indicating 6061 has better shape retention under stress. Elastic modulus, or stiffness, 6061 is slightly higher in 5052 (70.3 GPa), giving it marginally better resistance to bending. Finally, fatigue strength—critical for cyclic loading applications—is much higher in 5052 (117 MPa) than in 6061 (62 MPa), making 5052 more suitable for components that endure repeated stress.
Make Your Idea Take Shape!
Corrosion resistance
The corrosion resistance of 5052 aluminum is due to its high magnesium (Mg) content. Magnesium has a high solubility in the aluminum (Al) matrix, which minimizes the formation of secondary phase particles that could accelerate the corrosion of the alloy matrix. Additionally, the presence of chromium (Cr) in 5052 aluminum alloy effectively suppresses corrosion reactions, further enhancing its corrosion resistance. Similarly, the corrosion resistance of 6061 aluminum is attributed to the primary secondary phase in its microstructure being magnesium silicide (Mg₂Si). Since Mg₂Si has a lower potential than the Al matrix, it does not lead to preferential dissolution of the matrix, thus reducing the risk of corrosion.
Table 6. Corrosion resistance of aluminum 5052 and 6061
| Property | 5052 | 6061 |
| Composition | Aluminum-Magnesium | Aluminum-Silicon-Magnesium |
| Chloride resistance | Good | Moderate |
| Acid resistance | Good | Poor |
| Salt spray test | Slight pitting | Significant pitting |
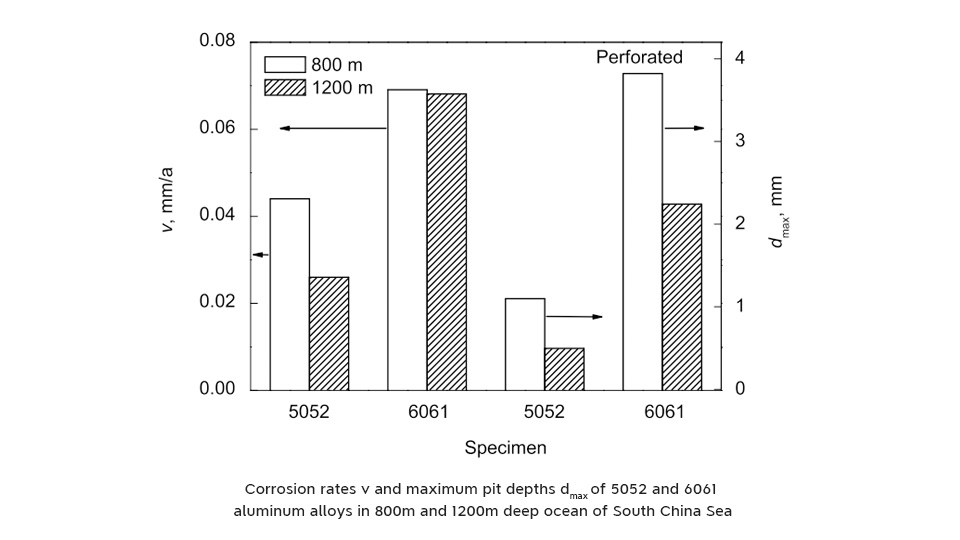
Sun Feilong and colleagues conducted corrosion experiments by placing 5052 and 6061 aluminum at depths of 800m and 1200m in the South China Sea. They found that 6061 aluminum exhibited more severe pitting corrosion than 5052. This increased susceptibility in 6061 was attributed to the significant micro-galvanic potential difference between the MgSi phase and the Al-Fe-Si matrix, which accelerated localized corrosion.
Weldability
In terms of weldability, both 5052 and 6061 are good, but 5052 is slightly better than 6061.
The mechanical properties that influence welding distortion are complex, with the thermal expansion coefficient having the greatest impact. Materials with a higher thermal expansion coefficient, like 5052 aluminum (23.75 x 10^-6/°C), expand and contract more dramatically during heating and cooling, making them more prone to welding distortion. However, 5052 has a lower yield strength (193 MPa) compared to 6061 (276 MPa), which results in lower residual stresses after welding, reducing the risk of cracking and brittle fractures. While 5052 has a slightly higher thermal expansion coefficient, its lower yield strength and higher ductility allow it to better withstand the stresses of welding, making it easier to weld overall.
Table 7. Weldability properties of aluminum 5052 and 6061
| Property | 5052 | 6061 |
| Thermal Conductivity, W/m·K | 138 | 167 |
| Elastic Modulus, GPa | 70.3 | 68.9 |
| Thermal expansion coefficient(10*-6/℃) | 23.8 | 23.6 |
Price
The price difference between 5052 and 6061 is mainly due to the proportion of their alloy components. The price of a 6061 aluminum plate is naturally higher than that of a conventional 5052 aluminum plate due to the complexity of the process and the different performance requirements of the process. The price of a 5052 aluminum plate is generally around 25.5 yuan per kilogram, and the processing fee is usually in the range of 3500-4500 yuan. Depending on the brand of the aluminum plate manufacturer and the equipment price of the enterprise, it will fluctuate in the entire price range. The price of a 6061 aluminum plate is generally around 27.5 yuan per kilogram, and the processing fee of one ton of 6061 aluminum plate is between 4600-8000 yuan.

Common applications
Here’s a quick overview of the industries and applications that typically use each alloy.
| Application | 5052 | 6061 |
| Marine | Ships, marine frames, LNG tanks | Marine frames, yachts, boat hulls |
| Aerospace | Aircraft fuel tanks, aerospace parts | Aircraft structural components |
| Automotive | Fuel lines, bus bodies, truck parts | Automotive frames, wheels, pistons |
| Construction | Curtain walls, roofing panels | Structural frames, rail platforms |
| Machinery | Pressure vessels, heat exchangers | Precision parts, machinery frames |
| Electronics | Enclosures, kitchen appliances | Enclosures, electronic connectors |
Conclusion
Both 5052 and 6061 aluminum are excellent materials, each with its strengths. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of your project:
- Choose 5052 if you need superior corrosion resistance, especially in marine or saltwater environments, or if you require a material that’s easy to form and weld.
- Choose 6061 if you need a stronger material that can withstand higher stress and is suitable for machining, structural components, and heat-treated applications.
By understanding the differences between 5052 aluminum and 6061 aluminum, China CNC machining manufacturers can make better-informed decisions that ensure the success of their projects. Whether you are working in aerospace, automotive, construction, or marine applications, knowing the properties and applications of these alloys can help you select the best material for your needs.