ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and PS (Polystyrene) are commonly used plastic materials. Although they are similar in appearance, there are significant differences in performance. ABS has excellent toughness and impact resistance, while PS is widely used because it is lightweight and easy to process. This article will compare ABS and PS from multiple perspectives including physical, chemical, and thermal properties to help you identify these two materials.
What is ABS?
ABS stands for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, which is a terpolymer of acrylonitrile(A), butadiene(B), and styrene(S). ABS is a widely used thermoplastic and engineering plastic. It is currently the polymer with the largest output and the most extensive application.
ABS has good impact resistance, heat resistance, and electrical properties. It can be used for post-processing such as metal plating, electroplating and welding. ABS is widely used in machinery, automobiles, electronic appliances and construction industries.

What is PS?
PS is the abbreviation for polystyrene, and it belongs to thermoplastics. Polystyrene is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. PS includes GPPS and HIPS.
PS is highly transparent with a light transmittance of more than 90%; it has characteristics of good electrical insulation, processing fluidity, rigidity, and corrosion resistance. PS is suitable for producing insulating transparent parts, decorative parts, chemical instruments, optical instruments, and other parts.

Differences Between ABS and PS
The table below shows the material properties of ABS and PS.
| Properties | ABS | PS |
| Tensile Strength, MPa | 37 – 110 | 32 – 44 |
| Impact Strength, J/m2 | 70 – 370 | 19 – 45 |
| Flexural Strength, MPa | 72 – 97 | 62 – 80 |
| Elongation at Break, % | 3.5 – 50 | 1.8 – 40 |
| Elastic Modulus, GPa | 2.0 – 2.6 | 1.9 – 2.9 |
| Thermal Expansion, µm/m-K | 81 – 95 | 80 – 98 |
| Heat Deformation Temp. ℃ | 82 – 100 | 70 – 90 |
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.0 – 1.4 | 1.0 |
ABS vs. PS: Physical Properties
The following will compare the strength, impact strength, flexural strength, elongation at break, and density to help you understand the different physical properties of ABS and PS.
Strength
ABS is stronger than PS. The tensile strength of ABS is generally 35-60 MPa, while the tensile strength of PS is 32-44 MPa. ABS can withstand greater external impact and extrusion without deformation. For example, ABS is used in electric shaver casings and small hair dryer casings.
Impact strength
The impact strength of ABS is 70 to 370 J/m2, while that of PS is 19 to 45 J/m2. ABS has higher impact resistance than PS. ABS has good toughness and impact resistance and can maintain shape when subjected to sudden impact. It can be used in products that may be impacted, such as tool housings and sports equipment. PS has poor impact resistance and is suitable for some products that do not require high impact.
Flexural strength
Flexural strength measures a material’s ability to resist damage under bending loads. ABS has a higher flexural strength. The flexural strength of ABS is between 72 and 97 MPa, and PS is between 62 and 80 MPa. ABS is stronger and less likely to deform when subjected to bending forces. It can be used for furniture accessories, electrical appliance brackets, etc.
Elongation at break
Elongation at break measures a material’s ability to plastically deform before being fractured. The elongation at break of ABS is 3.5 to 50%, while that of PS is 1.8 to 40%. ABS has greater deformability. ABS can deform greatly without breaking when subjected to force and has a certain degree of flexibility. It can be applied to products such as seals, hoses, etc.
Density
ABS has a density of 1.0–1.04 g/cm2, while PS has a density of 1.0 g/cm2. The two plastics have similar densities. However, ABS has higher impact strength and good ductility; its strength and durability are significantly better than PS despite similar weight.
ABS vs. PS: Chemical Properties
The following will compare the corrosion resistance, hygroscopicity, and UV resistance to help you understand the different chemical properties of ABS and PS.
Corrosion resistance
ABS has better corrosion resistance than PS. ABS has good chemical resistance to most acids, alkalis, and oils and can resist corrosion from various corrosive chemicals, but performs poorly in strong oxidants. PS has weaker chemical resistance and is particularly susceptible to getting dissolved or corroded by organic solvents, greases, and acids.
Hygroscopicity
The water-absorbing capacity of ABS is about 0.2-0.3%, while that of PS is lower, usually around 0.03%. PS is more stable in a humid environment.
UV Resistance
PS is more susceptible to UV rays than ABS. PS will turn yellow and become brittle when exposed to sunlight for a long time. ABS has better UV resistance, but surface treatment may still be required to improve durability if exposed to extreme UV environments.
ABS vs. PS: Thermal Properties
The following will compare the heat deflection temperature and thermal expansion to help you understand the different thermal properties of ABS and PS.
Heat deflection temperature
The heat deformation temperature of ABS is 80–100 °C, which is slightly higher than that of PS of 70–90 °C. ABS can maintain good dimensional stability at high temperatures, so it is suitable for high-temperature environments, such as home appliance housings. PS has a lower heat deformation temperature and is ideal for applications at room temperature, such as food packaging.
Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion measures the degree to which a material changes in size when the temperature changes. The thermal expansion of ABS and PS is similar, 81 to 95 µm/m-K for ABS and 80 – 98 µm/m-K for PS. Both need to take necessary design measures to reduce the impact of thermal expansion when used in applications requiring dimensional stability.
ABS vs. PS: Processability
ABS has good processing properties and can be injection molded, extruded, blow molded, etc., while PS can also be processed by these processes but has poor fluidity. ABS is more suitable for products that require complex shapes than PS.

How to Distinguish ABS and PS?
ABS and PS are two common engineering plastics, but they are often confused because of their similar appearance. To identify these two materials, the following will introduce several simple and effective methods to distinguish ABS and PS.
Burning test
The burning test can effectively distinguish ABS from PS. When ABS burns, the flame is yellow with a light blue edge, and the burning speed is slow. ABS usually goes out after leaving the fire. When PS burns, the flame is orange-yellow and accompanied by black smoke. PS burns faster and continues to burn after leaving the fire.
Solvent test
The solvent test is also a common method to distinguish ABS from PS. ABS has a strong tolerance to common organic solvents and will soften and not decompose quickly when encountering solvents such as acetone. In contrast, PS quickly dissolves or deforms when encountering benzene and ketone organic solvents (such as acetone). This difference makes solvent testing an effective means to distinguish the two.
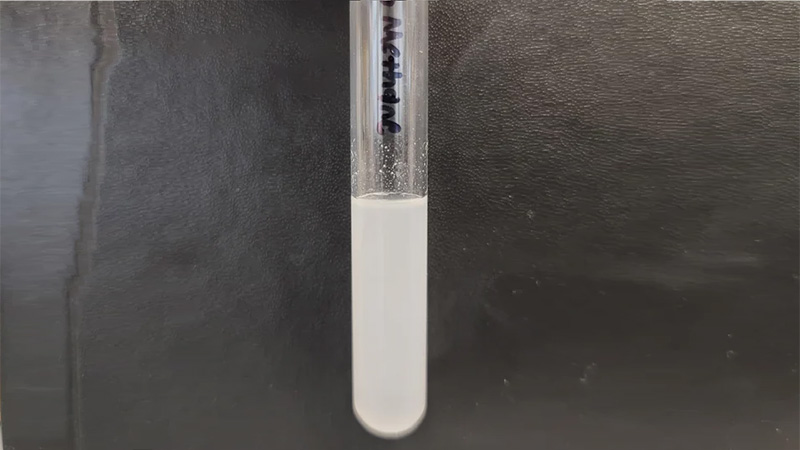

Density test
ABS has a density that is slightly heavier than water. When ABS is placed in water, it may sink. The density of PS is 1.0 g/cm3, which is the same as water. Most PS materials usually float on the surface of water. This simple sinking test can identify whether the material is ABS or PS.
Conclusion
ABS and PS have their unique characteristics in plastic applications. ABS is suitable for high-strength demand scenarios due to its excellent toughness, impact resistance and heat resistance, PS is widely used in packaging and daily necessities due to its lightness and easy processing. By comparing their physical, chemical and thermal properties, we can better understand the advantages and limitations of these two materials and help choose the most suitable application material.
At SogaWorks, our state-of-the-art machinists have a deep understanding of the various characteristics of plastics like ABS and PS. We’re here to assist you in selecting the ideal material for your custom project. Request a quote and receive DFM feedback today!