When talking about the finishing of metal parts, two of the common surface treatments discussed will be powder coating and anodizing. Both processes provide critical benefits such as corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetic appeal, but they achieve these in very different ways. This article explores the differences between these two processes, including their advantages, and performance, helping you make an informed decision on which method is right for your needs.
What is Powder Coating?
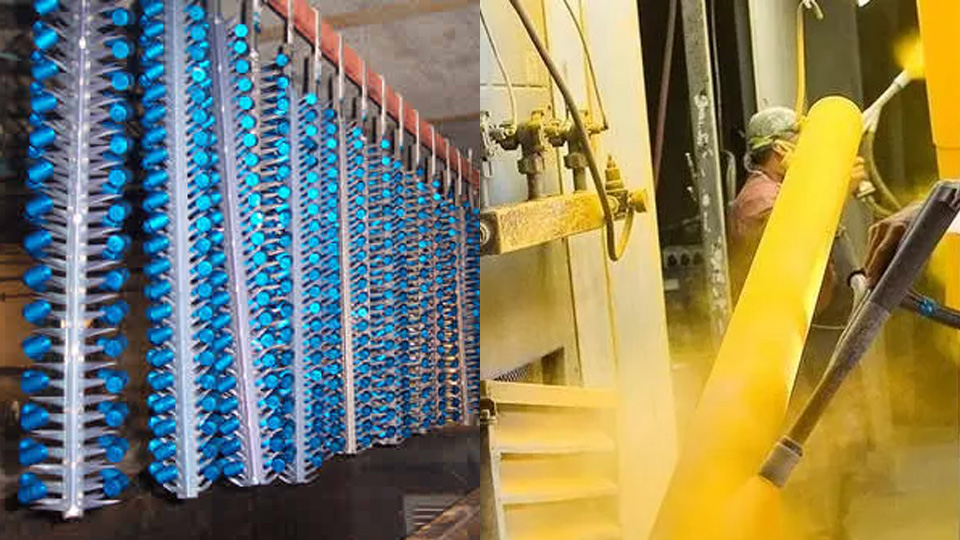
Powder coating is a finishing process in which a dry powder is applied to the surface of parts using electrostatic spraying equipment. The powder carries an electrostatic charge, allowing it to be evenly attracted and held onto the part surface. Once the powder has been applied, the powder-coated parts are exposed to high temperatures.
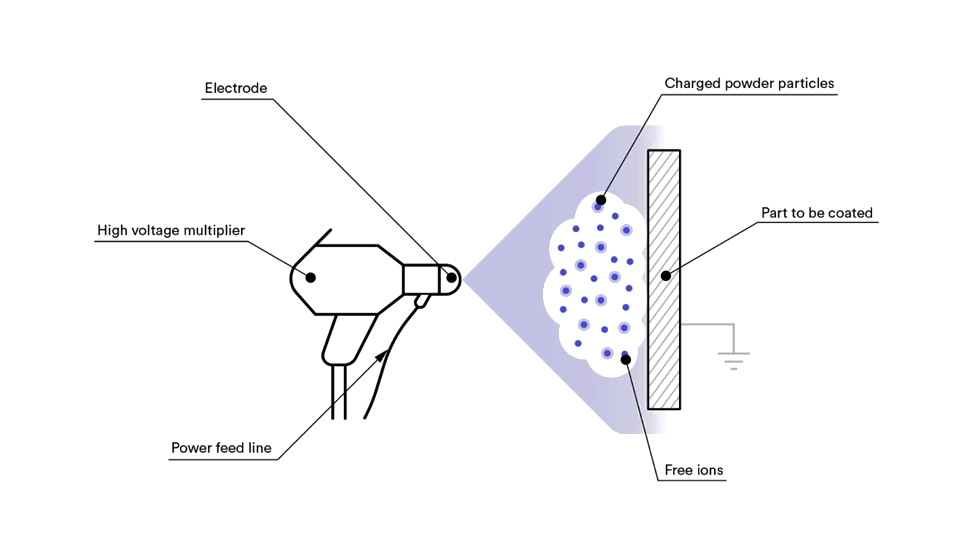
The coating is made of a special resin, pigment, filler, curing agent, and other additives, they are mixed in a certain proportion and then prepared by hot extrusion, crushing, and screening. They are stable in storage at room temperature, and after electrostatic spraying, heating, and solidification, a smooth and bright permanent coating is formed, to achieve the purpose of decoration and corrosion protection.
Advantages of Powder Coating
Increased efficiency. Since the film is formed in a single application, productivity can increase by 30-40% compared to traditional methods.
Energy savings. Powder coating reduces energy consumption by about 30%, making it more energy-efficient than conventional coating techniques.
Reduced Pollution. This process does not involve the emission of harmful organic solvents such as toluene or xylene, which are commonly found in paints, leading to less environmental pollution.
High coating utilization. The powder coating process boasts an excellent material utilization rate of over 95%, and excess powder can be recovered and reused, minimizing waste.
Superior coating performance. The thickness of the coating can reach 50-80μm in a single application. The adhesion, corrosion resistance, and other performance indicators of powder coatings typically outperform those of traditional paint processes.
High yield. Before curing, the coated items can be re-sprayed, ensuring a higher yield and better quality of the final product.
What is Anodizing?
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that produces a protective oxide by immersing metals ( aluminum) in an acid solution. The oxide film has a thickness of 8-120μm, which gives the aluminum parts resistance to corrosion and an aesthetic appeal.
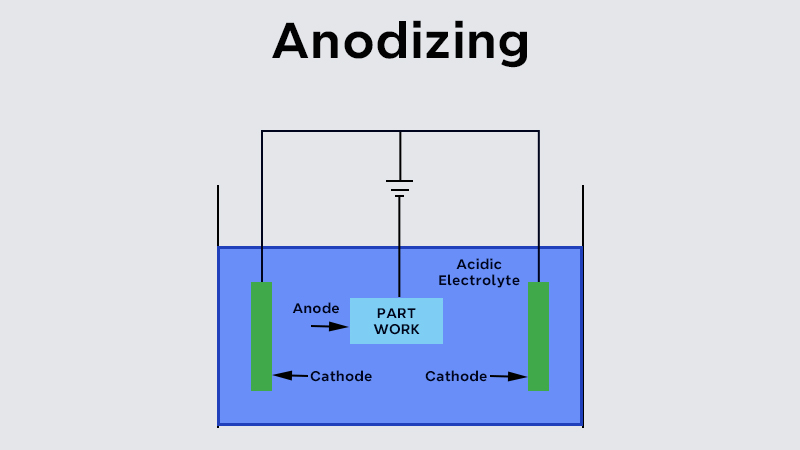
Unless otherwise specified, the anode in anodizing is usually made from aluminum or its alloy, and the cathode is a lead plate. The aluminum and lead plates are immersed in an acid solution containing sulfuric acid, oxalic acid, or chromic acid, where, through electrolysis, the surfaces of the aluminum get an oxide film.
Anodizing can be divided into 3 types: Clear anodizing, anodizing type II and anodizing type III.
Advantages of Anodizing
It improved corrosion resistance. Type II anodizing provides a protective oxide layer on the aluminum surface, it is able to protect aluminum from harsh environments such as moisture, chemicals, and saltwater. This improved corrosion resistance makes anodized aluminum an ideal choice for components exposed to mild or challenging environmental conditions.
Exceptional hardness. The oxide layer formed during Type III anodizing is much harder than that produced by Type II. It can reach a hardness of up to 60-70 HRC (Rockwell Hardness Scale), making it highly resistant to wear, abrasion, and scratching.
Enhanced durability. As the oxide layer is generated by a chemical reaction, unlike paint and coatings, it bonds precisely to the aluminum surface and is not easy to flake off.
Aesthetic appeal. Type II anodizing produces a porous oxide layer, this structure makes it possible to absorb various colors. The anodized aluminum surface can maintain its color over time. These aesthetically pleasing finishes bring designers more flexibility in aesthetics.
Anodizing vs Powder Coating: What are the Differences?
Process. Anodizing is an electrochemical process that uses electric current to form a layer of oxide. On the other hand, powder coating is an electrostatic spraying technology in which the dry powder is adsorbed on the surface by an electrostatic charge and then cured by heating to form a coating. These coatings are organic and consist of resins, pigments, and hardeners.
Substrate. Anodizing is usually used for specific metals such as aluminum and titanium, while powder coating can be applied to a wider range of materials, including metals like stainless steel, aluminum, plastics, wood, glass, etc.
Color and appearance. Color and appearance. Powder coating offers a broad range of color options by mixing pigments and curing agents. Anodizing acheives colored appeal by immersing the aluminum parts into a coloring solution before curing. Typically, powder coating has a wider range of color options than anodizing.
Durability. Anodizing forms a hard oxide film on the metal surface, which is tightly bonded to the substrate. The coating hardness can reach 300 HV (depending on the anodizing type), and the coating is not easy to wear or flake. Powder coating is cured on the surface of the part at high temperature, and is not as hard as the oxide layer. The coating is easily damaged by friction and scratches, and the coating may peel, crack, or wear.
Put Your Custom Parts into Production Today!
Corrosion resistance. Corrosion resistance is one of the key differences between anodizing and powder coating. The oxide layer formed by anodizing is not only hard but also provides excellent corrosion resistance by effectively isolating the substrate from the external environment. Anodized aluminum parts have excellent corrosion resistance when exposed to marine climates, high-humidity environments, industrial chemicals, etc. Powder coatings also provide some corrosion resistance, but they generally do not perform as well as the anodized when exposed to extreme environments. For example, when exposed to rain or salt spray conditions, the coating may crack and result in corrosion of the metal surface.
Cost. Anodizing generally costs more than powder coating. This is because anodizing requires specialized electrochemical equipment and higher energy consumption, while powder coating equipment is simpler and material costs are lower. For large-volume production, powder coating is usually a more cost-effective option. However, The additional cost of anodizing may be worth it in specific applications, especially where high durability and special protection are required.
Repair and maintenance. Once the anodized coating is damaged, it is difficult to repair. Since the oxide film is closely bonded to the substrate, scratches or damage on the surface cannot be easily repaired and usually require replacement or re-surface treatment. Powder coating, on the other hand, has a strong repair ability, especially when the coating is damaged, it can be restored to its original state by re-spraying.
How to Choose Between Them?
When selecting anodizing or powder coating, there are several critical factors to consider in order to choose the best and most cost-effective method for your application. Here are some key factors to consider:
Cost
Powder coating is generally less expensive than anodizing, especially for large production runs. The overall cost may slightly differ by factors such as part size, and the type of powder used. Anodizing requires specialized equipment and higher electricity consumption during the process, thus it costs more. However, Anodizing can provide enhanced durability and corrosion resistance for certain applications despite of higher cost.
Tips: Evaluate your needs, and choose a process that gives you the right balance between cost and performance for your application.
Color
Powder coating does not have any significant limitations when it comes to offering color variants. Since the colors can be added to the powder coatings by mixing them with a wide range of colorants, they can be colored-matched very precisely. Anodizing has more limited color options. The dyes used in anodizing are absorbed into the porous oxide layer, resulting in less vibrant and more muted colors.
Tips: For applications requiring specific or vibrant colors, powder coating is the better choice. If a metallic color is acceptable, anodizing may be sufficient.
Durability and resistance
Anodizing forms a layer of oxide that is bonded to the base material; hence, it can yield wear and resistance to harsh conditions. Powder coating applies a protective coating layer on the base material, it can also provide some corrosion resistance. But it bonds more loosely and is easier to scratch and flake.
Tips: For applications to be exposed to heavy tears and harsh environmental conditions, anodizing provides much better durability and protection.
Surface preparation
In anodizing, sandblasting is commonly used to clean the surface and remove impurities, ensuring good adhesion. Similarly, anodizing requires thorough cleaning before the process to avoid imperfections. Powder coating has lower requirements on the surface quality of raw materials. Powder coating can cover the extrusion lines on the surface of the profile, conceal some defects on the surface of the aluminum profile, and improve the surface quality of the finished aluminum profile.
Surface quality
Powder coating produces a smooth, shiny finish. This finish is visually to appear highly uniform and gives a sleek look. Anodizing provides a matte or satin finish since the process involves forming a porous oxide layer, which is not as smooth as the coating. The finish is generally more rugged.
Conclusion
Both powder coating and anodizing have their specific advantages, and the choice depends upon which factors are most important for your project. Powder coating has wide color ranges with intense colors, but more limited corrosion resistance and durability. Anodizing, on the other hand, provides hardness and resistance, especially where withstanding heavy wear is a factor. While anodizing is more expensive, it has better corrosion resistance and durability. It is better to consider several factors such as price, color requirements, and durability before you select one.
At Sogaworks, we specialize in delivering high-quality, precision CNC machining services from China and anodizing services tailored to satisfy the needs of our clients. We offer a comprehensive range of surface finishing services, including powder coating and anodizing. With our advanced equipment and expert engineers, we deliver durable, reliable, and cost-effective solutions for customers in various industries.






