In the 1980s, the CNC router was introduced by pioneering companies like Shopbot, it is primarily used for cutting non-metal materials like wood and plastics. Now it has been used to process parts in many industries. This article is about to discuss what a CNC router is, how it works, materials that can be cut, and prospects.
What is a CNC Router?
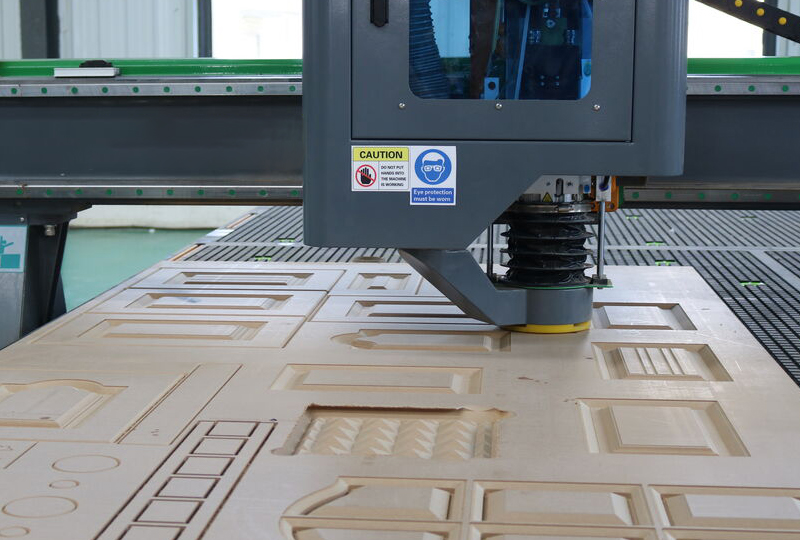
A CNC router, directed by computer programs and codes, is a machine used for milling, drilling, engraving, and routing. A CNC router was primarily used to cut wood but has now expanded to carving and cutting plastics, foam, glass, soft metals, and more.
CNC Routing vs. CNC Machining
The main differences between CNC machining and CNC routing are the material capability and cutting force. CNC machining generally refers to more robust machines like CNC mills and lathes, A CNC mill is designed for cutting harder metals and has slower speed and high cutting forces. However, a CNC router is mainly used for cutting soft materials like wood, plastics, and some soft metals like aluminum and copper. It has high speed and low cutting forces. The table below shows the difference between them:
| Criteria | CNC mill | CNC router |
| Marerials | Soft & hard materials | Mainly soft materials |
| Precision & Force | High precision, strong cutting force | Moderate precision, low cutting force |
| Speed | Slow | Fast |
Desktop CNC Router
The desk CNC router is a smaller, more compact version of a conventional CNC router. It provides the same basic functions as a larger CNC router, but on a smaller scale, primarily for lighter materials like plastics, wood, or soft metals. They are perfect for prototyping, hobbyists, or production on a small scale where budget and space are both limited.
How Does A CNC Router Work?
To use a CNC router to process a material, follow these steps:
First, use the CAD (computer-aided design) software to create the design you want to cut. Once the design is ready, switch to the toolpath program, which is also provided with the machine, to generate the cutting instructions. These instructions will guide the machine during the cutting process. Next, secure the material to the cutting bed, ensuring it stays firmly in place during operation. Afterward, install the correct bit. There are various types of CNC router bits. Finally, start the routing process. The spindle will move according to the programmed instructions, cutting along the three axes (X, Y, and Z) to execute the design. Ensure you monitor the process to make any necessary adjustments for accuracy.
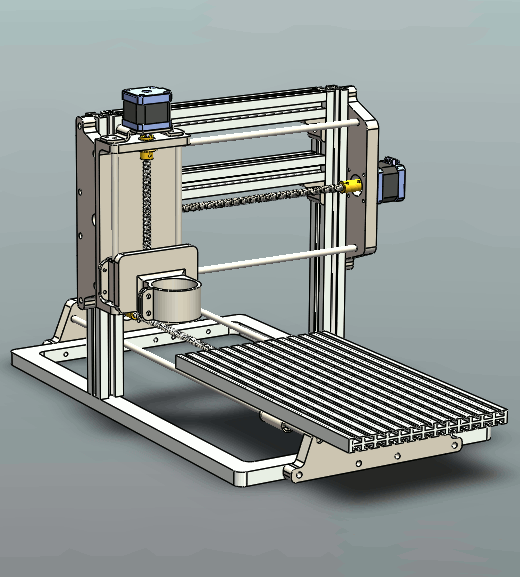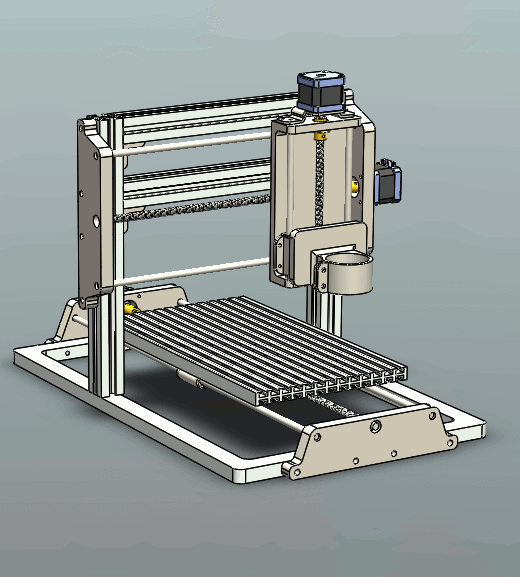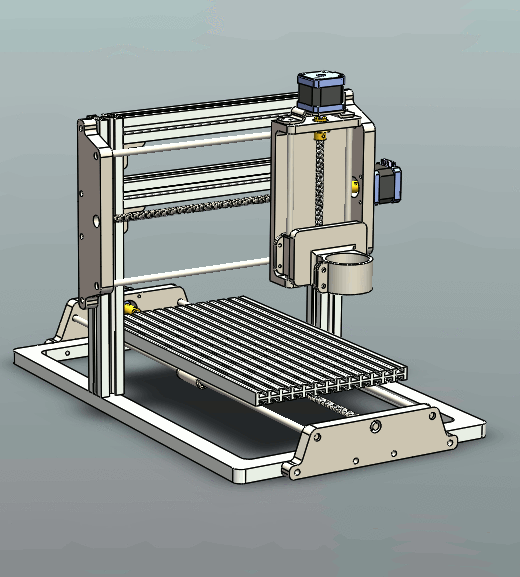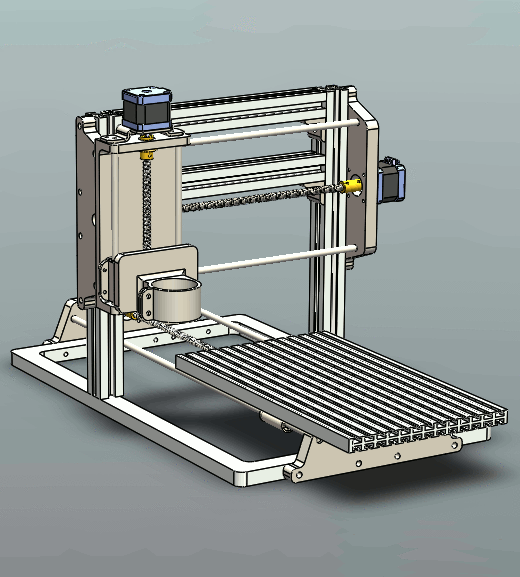
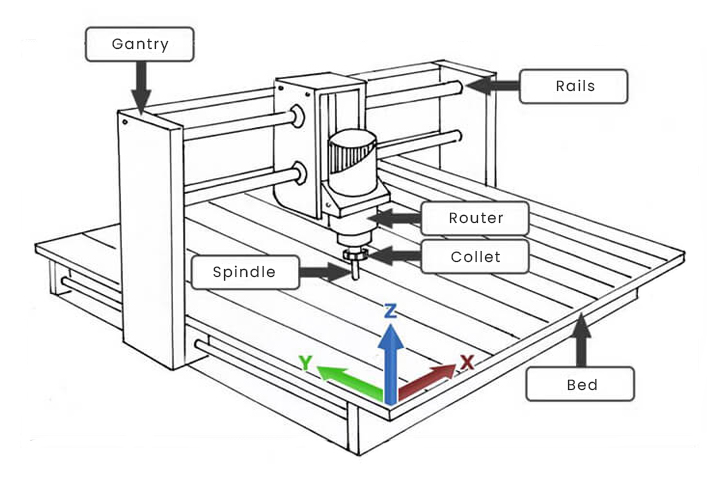
Key Components of CNC Router
The CNC router is comprised of 4 key components: cutting bed, spindle, drive system, and controller.
Bed is the flat, smooth surface that holds the material that is to be processed. Put the material you prepare to cut onto the bed and secure it in place by using clamps, screws, and adhesives.
Spindle is the blade that rotates and extends beyond the flat surfaces of the machine. It is the component of the machine that performs the cutting. It performs cuts by spinning its cutting tool at various speeds.
Drive system consists of the components of the CNC routing machine that allow it to move on three axes (x, three axes, namely y, x, and Z) while cutting. A drive system that is a single unit usually includes a motor bearing and mechanism to move (like a rack and pinion set-up).
Controller controls the drive system. If you have a plan to cut the material, you load it into the controller by using a post-processor to convert the file into the form of a geometric code (G-code). The controller then uses the G-code to control the drive system and perform the cutting on the material.
Materials Can Be Cut
A CNC router is capable of processing various materials. Here are some of the common materials that can be cut on a CNC router:
Wood: A CNC router is suited for cutting various types of wood. Softwoods like pine, cedar, and spruce; hardwoods like oak, maple, walnut, and cherry; others like polywood and medium-density fibreboard.
Plastics: CNC routers are effective for cutting many types of plastics. Such as acrylic, available in clear, colored, and frosted forms, PC, PVC, and ABSM HDPE.
Foams: Foams are another material that can be cut, such as polystyrene or EVA foam.
Soft metals: Although CNC routers are not typically used for cutting metals, they can handle some softer metals with the appropriate tooling. such as aluminum or brass.
Future of CNC Router
In the future, CNC router machines are bound to develop towards high performance, multifunction, customization, intelligence, and greenness.
High performance: As we have developed CNC routers, we’ve been striving for higher accuracy in processing in cutting speed, productivity efficiency, and reliability. Soon, CNC routers will achieve high-speed, high-precision, and high-speed direct interpolation of intricate surfaces and curves, as well as servo control with high dynamic response through further optimization of the machine structure, advanced control systems, and efficient mathematical algorithms by using digital simulation and optimization. Advanced rigidity and static design thermal stability control online dynamic compensation and other techniques greatly increase the accuracy and reliability.
Multi-function: Combining various cutting processes to the use of multiple techniques for forming and “machine-machine” integration and collaboration of CNC routers and robotics are advancing and evolving. From the traditional sequence of processes that is “CAD-CAM-CNC” to the one that is based on 3D solid models, the “CAD+CAM+CNC integration” one-step processing direction is evolving and extends the web made up of “machine-machine” interconnection to the direction of “man-machine-thing” interconnection and processing big data processing that is supported by cloud computing and edge computing.
Intelligent: By using sensors and standard communications interfaces, machine tool status and the machining process’s signals and information are detected and collected. The process of machining is taught by the processes of transformation, model analysis, and data mining. Information and guidelines are created to assist in making the best decisions, thus allowing control over the machine tools and processes. Monitoring, forecasting, controlling, and monitoring the process is in line with the demands of high-quality, effective, flexible, and adaptable processing. “Perception, interconnection, learning, decision-making, and self-adaptation” will be the primary capabilities that comprise CNC machine intelligence. Processing massive data in industrial IoT digital twins, cloud computing/edge processing, deep learning, and so on. will help in the future development of automated machine programs. Technology advancement and development.
Greening: The technology is orientated to the requirements of future sustainable development. It will include a green design, a light structure, energy-efficient and environmentally sustainable manufacturing, enhanced energy efficiency, a simple cutting technology, a comfortable human-machine interface, as well as green services throughout the product’s life cycle.






