CNC machining is an important part of modern manufacturing and is widely used to machine metal and plastic materials. However, due to the differences in the physical and chemical properties of metal and plastic materials, CNC metal machining is significantly different from plastic machining in many aspects. This article will analyze these two processes in order to provide a reference for technological applications in the manufacturing industry.
Material Properties And Necessary Steps
Metallic materials often exhibit elevated levels of hardness, strength, and toughness, along with excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. These attributes require increased cutting pressures and more accurate instruments for metal machining, as well as greater demands on the stiffness and stability of processing equipment. In order to guarantee the ultimate quality of the workpiece, it is imperative to rigorously regulate the deformation, heat treatment, and surface roughness of metal components throughout the manufacturing procedure.
Plastic materials often exhibit low levels of hardness, toughness, and heat conductivity while demonstrating favorable flexibility and formability. To prevent workpiece distortion and burning, plastic machining places a greater emphasis on controlling cutting speed and cutting temperature. In addition, plastic machining must take into account variables such as the thermal expansion coefficient, viscosity, and fluidity of the material in order to guarantee precise processing and a high-quality surface finish.
Equipment and Process
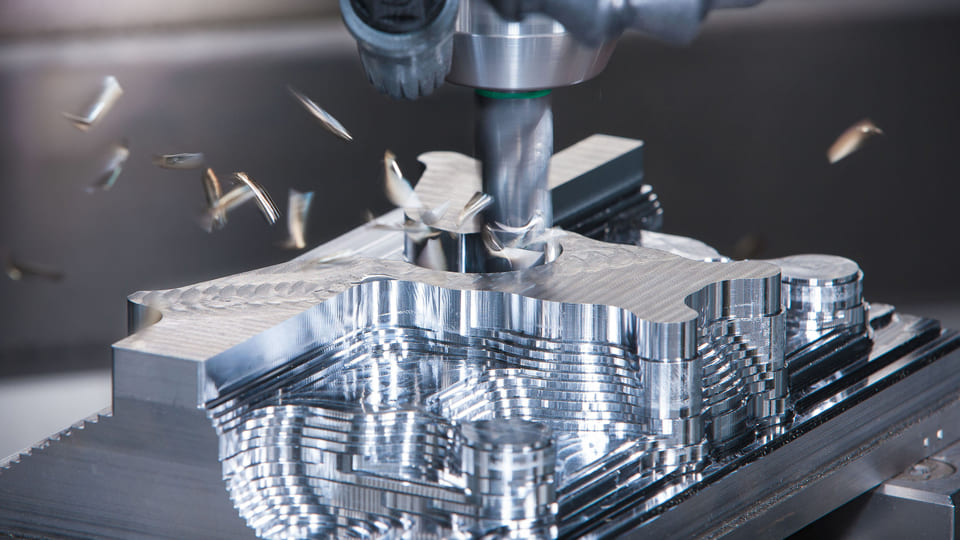
High-precision spindles, feed systems, and control systems are frequently used in CNC metal machining equipment to meet the demanding criteria of high accuracy and high efficiency. Precision control of cutting parameters and processing routes is essential for achieving accurate processing and high-quality surface finishes in operations like milling, turning, drilling, grinding, and similar processes. Furthermore, metal machining may include later procedures, such as thermal treatment and surface modification.

High-speed cutting and low-temperature cutting techniques. Machining procedures encompass many methods, such as milling, engraving, cutting, and so on. In order to prevent scratches and burrs, it is imperative to carefully choose the suitable equipment and cutting conditions. Furthermore, plastic machining requires careful consideration of the material’s thermal expansion coefficient and fluidity to ensure processing stability and precision.
Tool Selection And Deterioration
The selection of cutting tools in CNC metal machining has a direct impact on both the productivity of the operation and the quality of the output. To ensure optimal performance and durability, it is essential to select tools with high hardness and exceptional wear resistance, such as carbide tools and ceramic tools, based on the metal material’s specific hardness and processing requirements. Simultaneously, metal machining causes rapid wear on cutting tools, necessitating constant replacement and grinding of instruments to maintain processing accuracy and surface quality.
Tool selection holds comparable significance in CNC plastic machining. Because of the specific properties of plastic materials, it is important to use tools with sharp edges and low coefficients of friction, such as high-speed steel tools and diamond tools. However, working with high-hardness or high-toughness polymers typically accelerates the rate of tool wear during plastic machining. To mitigate tool wear and prolong its lifespan, it is imperative to carefully choose suitable tool materials and coatings, as well as establish optimal cutting settings.

Precision And Quality Control
CNC metal machining often necessitates precise machining precision and superior surface quality. High-precision spindles, feed systems, and control systems, along with appropriate tools and cutting settings, can help achieve micron-level machining accuracy. Furthermore, metal machining necessitates meticulous quality control measures, such as dimension measurement and surface roughness testing, to ensure that the workpiece adheres to the specified design criteria.
While CNC plastic machining may not demand the same level of processing precision as metal processing, it is nevertheless crucial to maintain processing stability and repeatability. Optimizing cutting parameters and processing procedures, along with the careful selection of suitable tools and processing equipment, can enhance the precision and smoothness of plastic machining. Furthermore, in plastic machining, it is critical to consider the influence of the material’s thermal expansion coefficient and fluidity on processing precision.
Conclusion
CNC metal machining and CNC plastic machining are significantly different in terms of material properties, machining equipment, tool selection, accuracy and more. CNC metal machining focuses more on cutting force and tool wear resistance, whereas CNC plastic machining focuses more on controlling cutting speed and temperature. In the future, metal and CNC plastic machining will pay more attention to environmental protection and sustainable development with increased environmental awareness and technological advancement.