In the dynamic landscape of the medical sector, innovation and precision are the driving forces behind the development of medical devices that save lives and enhance patient care. At the heart of this innovation lies the remarkable process of plastic injection molding. In this article, we discuss the advantages of injection molding, its suitable materials, applications, and certification and regulations in the medical industry.
Injection Molding in the Medical Industry
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that involves the production of parts and products by injecting molten material, typically a thermoplastic or thermosetting plastic, into a mold cavity. The material is heated to its melting point and then injected into the mold under high pressure, where it cools and solidifies to take on the shape of the mold.
Plastic injection molding is critical for the medical industry due to its ability to provide precision and consistency in the production of medical devices and components. The method's capacity to create intricate and complex part designs with unmatched accuracy is indispensable in a field where the slightest variation can have a significant impact on patient safety and treatment outcomes. Furthermore, injection molding's efficiency in high-volume production is instrumental for the cost-effective manufacturing of disposable medical supplies, helping to meet the surging demand for healthcare products and respond swiftly to medical emergencies.
Benefits of Plastic Injection Molding
Medical injection molding offers numerous advantages, Here are some key advantages:
Precision and Consistency: Injection molding allows for the creation of complex, precise, and consistent components, which is critical in the medical field where the accuracy of devices can impact patient safety and treatment outcomes.
High Volume Production: It's well-suited for high-volume manufacturing, enabling cost-effective production of medical components, which is especially important for disposable medical devices and supplies.
Cost-Effective: The ability to produce high volumes of medical components cost-effectively contributes to reducing healthcare costs, making medical services more accessible.
Fast Production: Injection molding offers quick turnaround times, ensuring that medical devices and components can be manufactured rapidly to meet market demand and respond to emergencies.
Longevity and Durability: Components manufactured through injection molding are often durable and reliable, which is essential for the longevity and performance of medical devices.
Patient Safety: With its precision, consistency, and use of biocompatible materials, injection molding plays a significant role in ensuring patient safety by producing reliable and safe medical devices.
Low Contamination Risk: The closed system of injection molding minimizes the risk of contamination, making it suitable for producing sterile medical components.
Different Processes for Medical Plastic Injection Molding
The specific process and materials chosen may vary depending on the requirements of the aerospace application. Here are some common types of processes for plastic injection molding in aerospace.
Thermoplastic Injection Molding
Thermoplastics can be reheated and reshaped multiple times without undergoing significant chemical changes. Thermoplastic injection molding is a manufacturing process in which thermoplastic materials are heated to a molten state and then injected into a mold cavity. Once in the mold, the material cools and solidifies to form a plastic part or component.
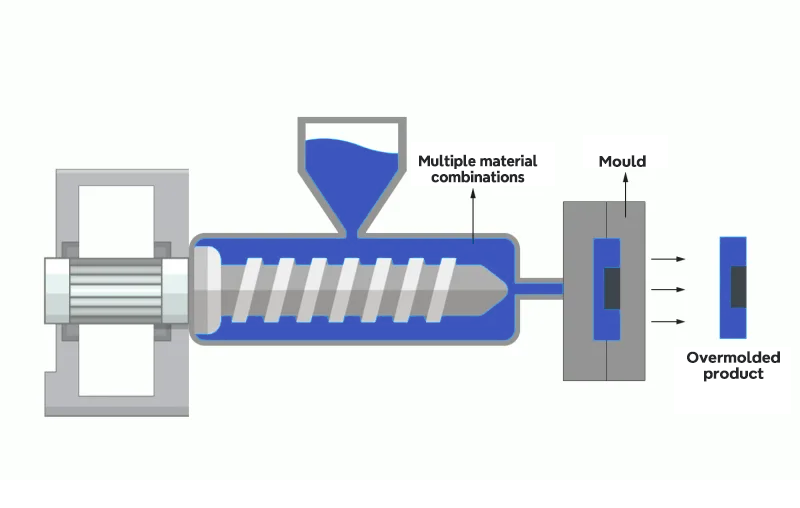
Overmolding
Overmolding is a plastic injection molding process where one material is molded over another, creating a single component with multiple properties. Typically, a soft or flexible material is molded over a rigid one to create a part with varying levels of flexibility and rigidity in different areas.
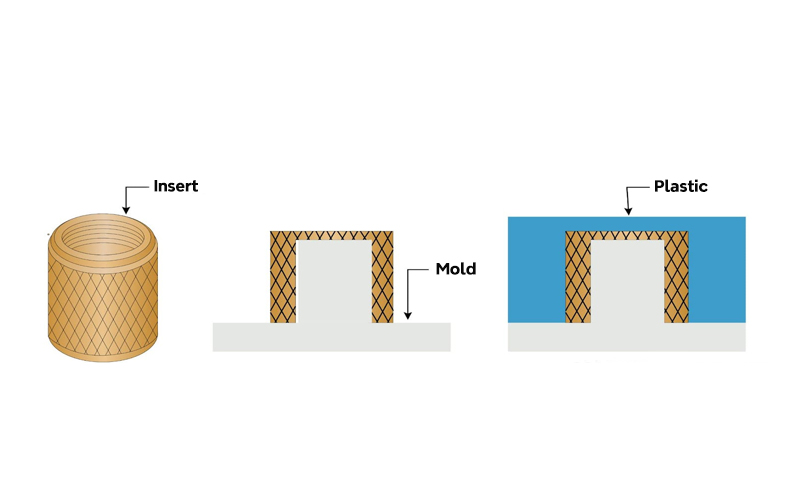
Insert Molding
Insert molding is a plastic injection molding process in which metal or other components (inserts) are placed into the mold before injection. The plastic material is then injected around and over the inserts, forming a secure bond between the plastic and the inserts.
Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding
The liquid silicone rubber(LSR) material is typically two-part, consisting of a base component and a catalyst that initiates the curing process. Liquid Silicone Injection Molding is a manufacturing process in which LSR is heated and injected into a mold cavity at high pressure. When injected into the mold, the LSR material undergoes a chemical curing process that results in a solid, elastic, and durable silicone rubber part.

Materials Used in Medical Injection Molding
Medical injection molding often employs a range of specialized materials to meet the strict requirements of the healthcare industry. These materials are selected for their properties such as biocompatibility, sterilizability, and strength for various medical applications.
What Properties Do Medical-grade Materials Have
Biocompatibility: Medical-grade plastics are biocompatible, meaning they do not cause harmful reactions or toxicity when in contact with the human body. They are extensively tested for their compatibility with living tissues and fluids.
Sterilization withstands: Numerous medical devices must maintain sterility, ensuring they are devoid of any contaminants or microorganisms that could pose risks to patients. Therefore, Plastics are required to withstand various sterilization methods, including autoclaving, gamma irradiation, ethylene oxide (EtO) sterilization, and electron beam sterilization, without degrading or compromising their structural integrity.
Regulatory Compliance: When designing components for medical equipment, the first thing to consider is its compliance with the appropriate authority, such as the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) or European Medicines Agency (EMA) requirements, to ensure their safety and efficacy in medical applications. These standards encompass factors like biocompatibility with biological tissues and the capacity to endure harsh physical and chemical conditions. Additional criteria are also subject to these regulations.
Strength and stability: In the realm of medical plastics, strength and durability are essential qualities. These materials are designed to exhibit both robust mechanical strength and long-lasting durability, ensuring the reliable and extended performance of medical devices and components while withstanding the rigors of clinical use.
Materials Used in Plastic Injection Molding
PC: Polycarbonate (PC) is a transparent and durable thermoplastic used in medical injection molding. PC offers exceptional impact resistance and clarity, making it suitable for medical applications that require transparency and the ability to withstand harsh sterilization methods. Its biocompatibility and resistance to chemicals contribute to its frequent use in medical devices and components.

PEEK: Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility. Its outstanding mechanical strength and resistance to harsh sterilization methods make it a preferred choice for medical implants and devices that require long-term reliability in clinical settings.
PE: Polyethylene (PE), in its various forms, is a versatile material employed in medical injection molding. It is known for its lightweight nature, chemical resistance, and ease of molding. PE finds applications in medical packaging, bottles, tubing, and other components that require compatibility with various medical substances.
PP: Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic with high chemical resistance and is commonly used in medical injection molding. PP's suitability for medical applications such as syringes, vials, and packaging is attributed to its ability to maintain its structural integrity when exposed to a range of pharmaceutical agents and sterilization methods.
Silicone: Silicone, a thermosetting polymer, is an ideal material for applications within the demanding and regulated field of medical manufacturing, due to its unique properties such as biocompatibility and excellent flexibility.
Applications of Medical Injection Molding
Medical injection molding is used to create a wide range of medical tools and devices by injecting melted materials into precise molds. It can be used for both on-demand prototyping and high-volume manufacturing of medical devices. Here are some common examples of medical injection molded parts:

- Implantable components: Like intraocular lenses, implants for joints, including hip and knee replacements, and medical-grade silicone implants for breast augmentation or reconstruction.
- Surgical equipment and components: surgical instruments, sterilizable surgical tools, etc.
- Orthopedics: Implants for orthopedic, prosthetic limbs and sockets, etc.
- Medical and laboratory equipment: Blood glucose test strips, specimen containers, diagnostics and testing equipment, etc.
- Syringes: Syringe barrels and components, injection pens, etc.
What to Know About Regulations and Compliance
Manufacturers of medical devices and components, through the process of injection molding, must navigate a complex regulatory landscape to ensure that their products meet rigorous quality and safety standards. Several key standards and regulations play a vital role in this industry, including:
FDA Regulations (U.S.)
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) sets stringent requirements for medical devices. Manufacturers must adhere to the Quality System Regulation (QSR) outlined in 21 CFR Part 820, which establishes the framework for good manufacturing practices (GMP) specific to medical devices. Compliance with FDA regulations is essential for marketing medical products in the United States.
ISO 13485 Certification
ISO 13485 is an international standard for quality management systems in the design and manufacture of medical devices. It encompasses various aspects, including risk management, design control, and process validation, all of which are critical in the medical injection molding process. Compliance with ISO 13485 is a globally recognized demonstration of a manufacturer's commitment to quality and safety.
ISO 10993 Certification
ISO 10993, often referred to as "Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices," is a set of international standards developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards provide guidelines and requirements for assessing the biological safety of medical devices, ensuring that they do not pose harm to patients or users. Some key aspects of ISO 10993 include biological safety assessment, biocompatibility testing, and risk management.
Summary
This article has introduced plastic injection molding in the medical industry, discussed its benefits, suitable materials, and applications. For in-depth knowledge and further insights into plastic injection molding, feel free to get in touch with SogaWorks.
SogaWorks offers an extensive range of manufacturing capabilities, including injection molding services and other exceptional manufacturing services to address your prototyping and production needs. Check out our official website and get an instant, hassle-free quote.








