Embarking on a CNC machining journey, where precision and creativity intersect. Among the crucial decisions in this manufacturing is choosing between the dimensions of axis movement—3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis machining —each with its own set of moves, offering a spectrum of possibilities for crafting intricate components. In this article, we unravel the distinctions between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining, navigate through the intricacies of their movements, and explore the factors that guide the choice between them.
What Is 3-axis Machining?
3-axis CNC machining involves a milling or machining process where a computer controls the movement of a cutting tool in three directions: along the X-axis (side-to-side), Y-axis (front-to-back), and Z-axis (up-and-down). This technology is commonly used for producing parts with relatively simple geometries.

3-axis CNC machining is an ideal choice for industries requiring precision in straightforward shapes. However, its limitation lies in the complexity of producing intricate, three-dimensional designs. The machine's tool is constrained to three directions, making it challenging to reach undercuts or intricate contours without additional setups. For projects demanding a more intricate approach, higher-axis CNC machines may be more suitable.
What Is 4-axis Machining?
Compared to traditional 3-axis machining, 4-axis machining introduces an additional rotational axis, commonly referred to as the A-axis. The A-axis enables the workpiece to rotate automatically around the X-axis, allowing for the machining of all four sides of the piece in a single setup, while it remains secured in the fixture.
4-axis machining effortlessly handles features like helixes, arcs, as well as other complex geometries. The introduction of the A-axis reduces setups, thereby enhancing precision. However, since the piece is fixed in a single setup for the 4th axis, features at angled need to be on the same axis. Otherwise, adjustments for each angle setting may be necessary for features at different angles.
What Is 5-axis Machining?
5-axis CNC machining means the ability to manipulate a workpiece simultaneously from five different sides. In addition to automatic movement along the X, Y, and Z axes, a 5-axis CNC machine can choose to use two of the three rotational axes (A-axis, B-axis, C-axis). The A-axis, B-axis, and C-axis rotate around the X-axis, Y-axis, and Z-axis, respectively. This capability allows the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from virtually any direction, offering enhanced flexibility for machining complex geometries, intricate curves, and features that require multi-angle approaches.

5-axis CNC machining typically includes 3+2 CNC machining and simultaneous 5-axis CNC machining.
3+2 CNC Machining
3+2 CNC machining, also known as positional 5-axis machining, is a machining technique that combines elements of both 3-axis and 5-axis machining. In this approach, 2 rotating axes of the 5-axis machine are used to fix the workpiece in a tilted position, then execute operations of 3-axis CNC machining. While the workpiece remains fixed during cutting, these two rotational axes offer the flexibility to approach the material from various orientations. This method allows for more intricate and precise machining of complex geometries without the cost and complexity associated with full 5-axis simultaneous machining.
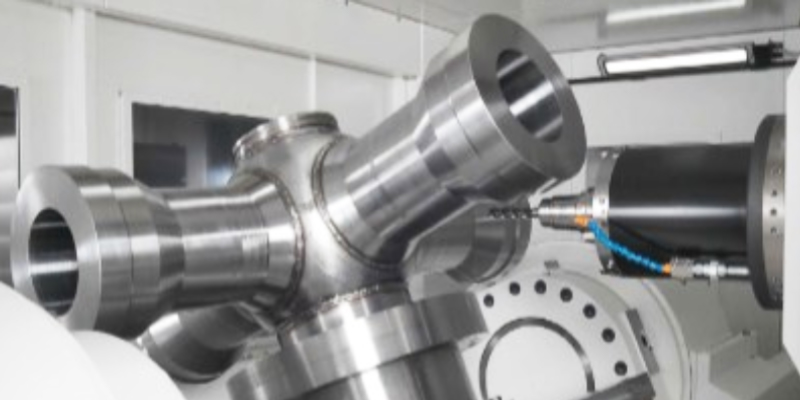

Simultaneous 5-axis CNC Machining
Simultaneous 5-axis CNC machining is an advanced manufacturing process in which a cutting tool moves across five different axes simultaneously to create complex and intricate geometries. The five axes include the traditional X, Y, and Z linear movements, as well as two rotational axes (usually denoted as A and B). Unlike 3+2 CNC machining, simultaneous 5-axis machining allows all five axes to move simultaneously during the cutting process. This capability enables the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from multiple angles and orientations in a continuous and fluid motion. Simultaneous 5-axis machining is particularly beneficial for the production of highly complex components, such as aerospace components, turbine blades, and medical implants, where precision and intricate geometries are critical.
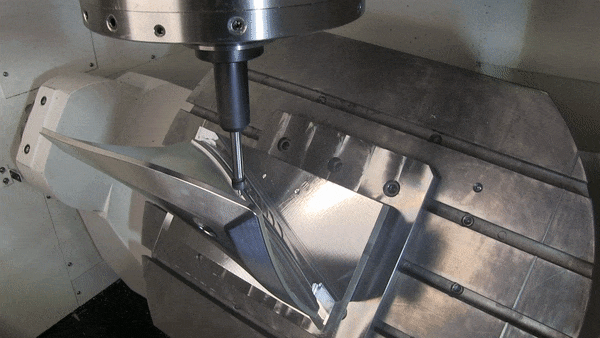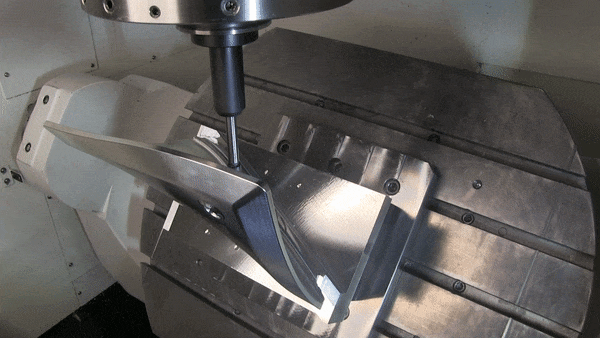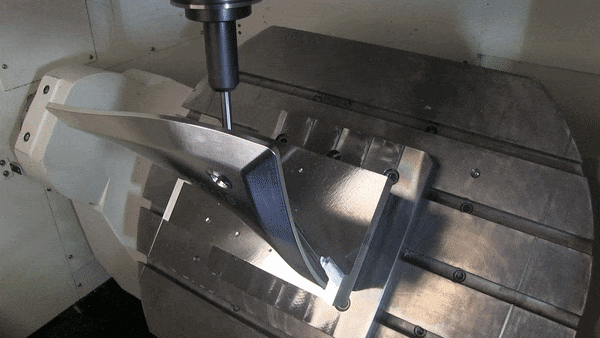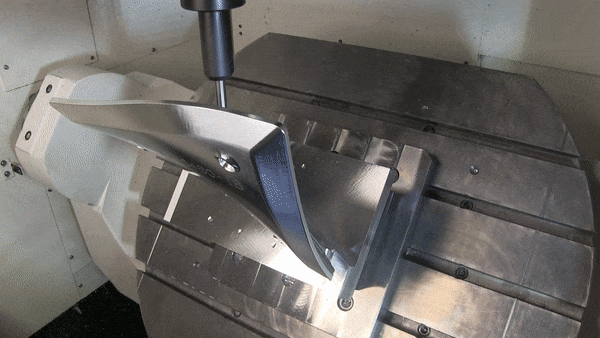
How to Choose Between 3-axis, 4-axis And 5-axis CNC Machining
Choosing between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining depends on the complexity of your project and the intricacy of the parts you need to produce. Here are key considerations to help you make an informed decision:
Part Complexity and Geometry
Evaluate the complexity of your parts and the intricacy of the required geometries. Choose an axis configuration that aligns with the complexity of your designs.
Precision and Surface Finish
Consider the precision and surface finish requirements of your parts. Higher-axis machines generally offer better precision and superior surface finishes, which can be crucial for certain applications.
Production Efficiency
Assess your production volume and speed requirements. Higher-axis machines often provide greater efficiency, especially for complex parts, by reducing the need for multiple setups.
Cost Considerations
Evaluate your budget constraints and weigh them against the capabilities offered by each axis configuration.








